Today I will provide you with the info about the motherboard of a computer. Also, the answering the questions like – what is a motherboard? where is the motherboard located? what does the motherboard do, its components, as well as, the purpose of the motherboard in personal computers.
The motherboard is undoubtedly one of the most important elements while assembling a computer. In a nutshell, the motherboard is spine of your computer.
In this article, I will explain what a motherboard consists of, its types, and the list of significant components that make it up a motherboard. So let’s see in detail what is a motherboard with pictures and everything you need to know about motherboards in an easy-to-understand manner.
What is a Motherboard?
In computing, the motherboard is the main integrated circuit card, that has all the slots and connections to which the rest of the parts of a computer are connected so that the computer system works properly.
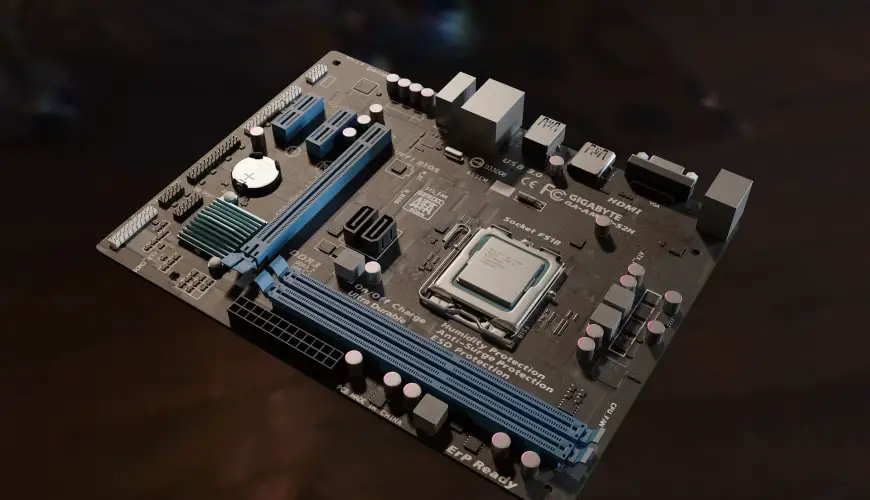

It is, therefore, a fundamental part of the PC case, where it has outlets to the outside that allow the connection of different peripherals and accessories, for a computer to function at full capacity.
The motherboard can be said to be the basis of a personal computer since the essential components such as CPU, graphic card, RAM, hard drives, expansion slots, CMOS, Mouse, Keyboard, and the power supply are directly connected to it. You can say the motherboard is the foundation of the computer itself.
The BIOS firmware is the permanent software installed on the motherboard, that allows regulating and testing the elementary functions of the hardware and acts as a support for loading the various operating systems like Windows, Mac, Linux, and others.
In short, the motherboard is where you’ll find the network of highways for transporting information throughout the entire system.
Apart from raw digital data, this includes information in the form of the electronic signals which your computer’s various components use to communicate through data buses managed by the chipset or processor.
How can you define computer motherboard?
Definition of Motherboard:
The motherboard is a ‘Main Printed Circuit Board (PCB)’ present in the computer cabinet where the various components such as a processor, RAM and ROM memory, hard drives, modular or non modular power supply, and among others, are interconnected, through which the electronic signals transform throughout the entire computer system to work optimally.
Where is the Motherboard located?
The motherboard is located in the PC case which is also known as a computer cabinet or chassis. Even if you know next to nothing about computers, you won’t have any trouble locating it as it is literally the largest PCB inside your laptop or computer case. As you can see in the image below.
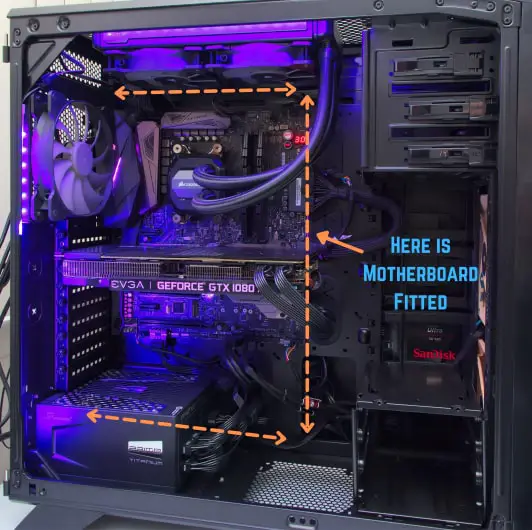

It needs to be as its job is to connect all the essential and auxiliary components, devices, and peripherals that comprise your computer unit.
Why does a Computer need a Motherboard?
No matter how fast the RAM, processor, video card, and data storage devices are, they themselves are a bunch of computer hardware. To turn it into a working machine, you need a platform that unites all the components into a working system unit. This function is performed by the motherboard.
In addition to internal slots, for connecting the main components, connectors for connecting external devices and peripherals are also soldered on the PCB. Therefore, the motherboard also integrates all devices into a fully functional computer.
Finally, Your system board is responsible for the sound of the computer, because it is built with a sound card and. And also for access to the Internet, due to the built-in network adapter which is also built-in.
Simple Fact about Motherboard:
Strictly speaking, the motherboard itself is just a bare PCB filled with zigzagging connections. But while it has no electric or processing power, it facilitates the work of your main processors and connects them to everything else on the system. For efficiency, the main components of your computer are often soldered or socketed directly onto your motherboard.
What are the Different Names for Motherboard?
The motherboard is known by many other names:
- Mainboard,
- Baseboard,
- Main Printed Circuit Board (PCB),
- System Board,
- Logical Board,
- Printed Wired Board (PWB).
What size and shape do motherboards have?
The size of motherboards is called “Form Factor”, and you should not be fooled by their dimensions, taking them as a reference of their capacity, since their size is independent of their power.
This means, you can find from small but very powerful motherboards, with a capacity of upgrading the number of RAM bar and support for multi core processors, to the large baseboard with little power.
Basically, the aforementioned “Form Factor” only determines where you will be able to locate said motherboard. In the case of having a large cabinet, you can choose a Form Factor ATX or microATX, on the other hand, if you want to build a computer in a small cabinet, you can choose a Form Factor ITX.
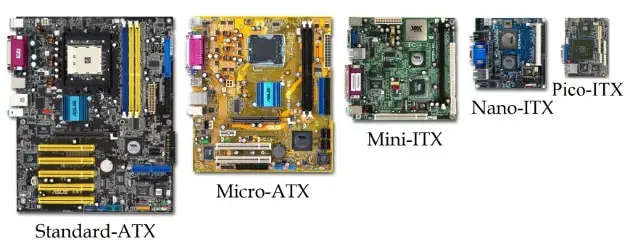
The choice of motherboard and its form factor depends on the choice of the case. The table below summarizes the list with all the approx corresponding dimensions for different types of computer, with the Form Factor, of the most modern motherboards on the market.
Form Factor | Dimension (L×W) |
Ultra ATX | 367×244 mm |
BTX | 325 x 267 mm |
EATX (Extended) | 305×330 mm |
ATX | 305 x 244 mm |
MiniATX | 284 x 208 mm |
MicroBTX | 264 x 267 mm |
MicroATX | 244×244 mm |
Mini-DTX | 203×170 mm |
MiniITX | 170 x 244 mm |
NanoITX | 120 x 244 mm |
ETX | 114×95 mm |
What are the types of Motherboard?
Now that you know what is a motherboard, let’s see its types. Motherboards are available in a variety of features and capabilities for different microcomputers, and these capabilities mainly depend on the motherboard manufacturers.
So there are no specific kinds of motherboards. But on the basis of motherboard structure, is divided into two parts:
- Integrated Motherboard
- Non-Integrated Motherboard
- Integrated Motherboard
Integrated motherboards are those motherboards in which multiple ports are available to connect various devices.
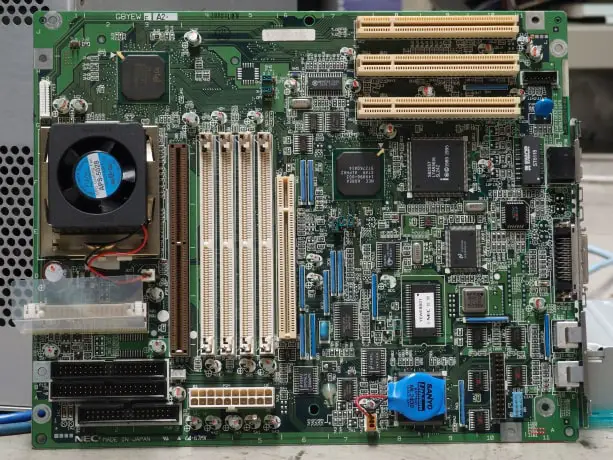

Integrated Motherboard allows the user to upgrade or modify the system computer either by making any changes or installing/connecting additional components like RAM, the graphics card, video card, sound card, and other controllers that can be upgraded in Integrated Motherboard.
The Integrated Motherboard is usually found in desktops, servers & laptops.
- Non-Integrated Motherboard
Non-integrated motherboards are those motherboards that are permanently fitted inside the computer system with no extra ports for the connection additional components.
No change or upgrade can be done in this type of motherboard. One cannot install additional components like graphics cards, RAM, and ROM memory on nonintegrated motherboards.
The Non-Integrated Motherboard is usually found in like Laptop, Smartphones & Tablets.
What is the Difference Between Motherboard and CPU?
CPU or Central Processing Unit carries out a computer’s instructions and controls all the arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations while the motherboard provides connections for all the computer components so that the electronic signals transform throughout the entire computer system to function properly.
Major Components of Motherboard
If you ever have the opportunity to carefully analyze a motherboard, you will discover that it has multiple parts and all of them are of great importance, for the proper functioning of the entire computer system that it controls.
Now that you know what is a motherboard, let’s see the list of major components of a motherboard that make it up. The major components of a motherboard are:
1. Chipset
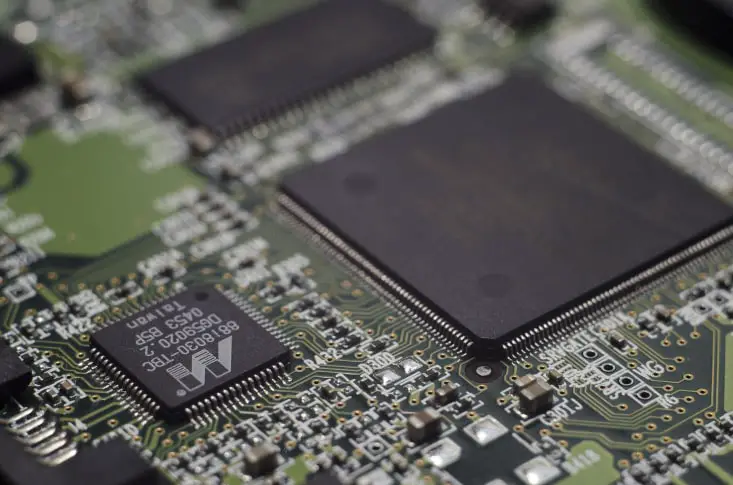
The chipset is a set of integrated circuits that are designed to establish and manage communication between the processor and the other components installed on the motherboard.
It typically handles processor communication with some expansion slots, storage drives, and ports for input devices and output devices of the computer.
The chipset, which is the communications centre for the entire computer. It is not entirely responsible for all data communications, but it is responsible for many interactions between the card and the other components of the computer.
Note: These chips are exclusively designed for the specific set of processors or a certain brand and for certain RAM memory modules. This makes it necessary that when acquiring a motherboard on the market we are forced to also buy a compatible processor and RAM memory modules for it.
In addition, the chipsets of each of the manufacturers are usually updated with each new generation of computers and types of processors. Currently, the Intel and AMD chipsets are the most commercialized in the market.
2. CPU Socket
A socket is a hole where the processor or CPU is inserted. It is an interface with the physical connectors that will be necessary to communicate with the motherboard. With the help of a special latch, the microprocessor can be embedded in the socket.
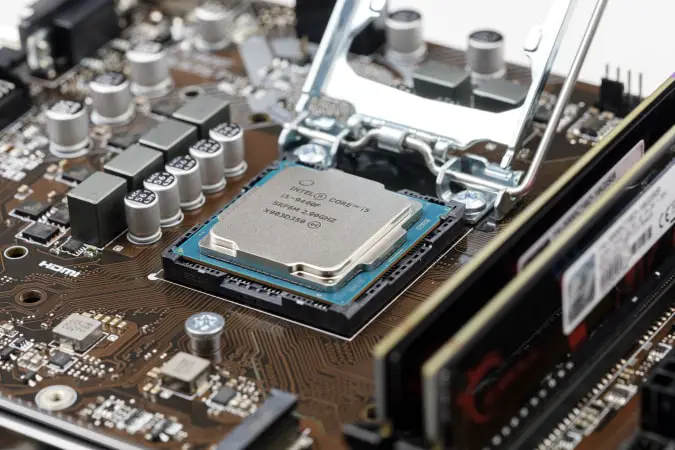

After installing, it establishes the connection between the processor and the motherboard. The socket is one of the main parameters when assembling a computer. As with processors, there are many types of CPU sockets for installation, so, it is necessary to acquire a processor compatible with it.
In addition, each motherboard is designed for a processor manufacturer, so both the socket and the chipset must be compatible with the brand in question.
3. RAM Slots
The motherboard also has a series of slots for connecting random access memory (RAM). The RAM memory slots are easy to identify and are usually close to the processor serving to accommodate modules of such processing memory.
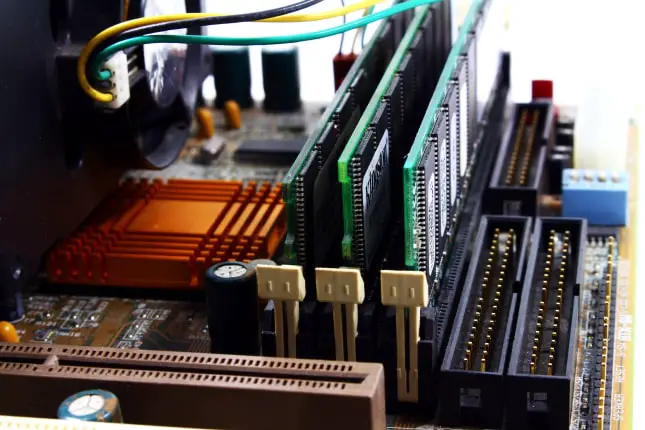

They are usually arranged in pairs and have certain specifications that define the type of RAM modules that can be used in the computer. These connectors or buses are responsible for housing the RAM memory modules that will be installed in the equipment.
In general, the motherboards have 4 slots or the high-end ones with 8. The maximum number of slots available depends on the motherboard. The number of slots, their type, and compatibility, will allow us to have more or less RAM in our computer, with which to run all the programs.
4. BIOS
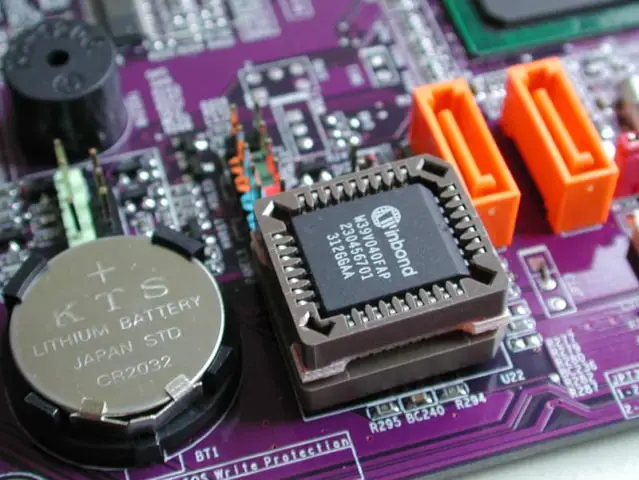
The motherboard’s firmware (permanent software) is typically stored in a ROM memory chip embedded on the motherboard, known as the basic input-output system (BIOS) system.
The motherboard is also home to the complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) chip. This is a standard component in modern digital electric circuits.
The BIOS provides the basic input-output functionality of the system. This software is what your PC uses to engage the boot and POST (Power on Self Test) process. By accessing the BIOS system, you can control the internal processes in your CPU, GPU, RAM, and other essential components.
In addition, it is in charge of checking the errors or absence of devices, for example, lack of RAM, CPU connection or Hard disk storage, among others.
From which it also allows you to troubleshoot basic problems, configure the order of drives to read upon booting, controlling any auxiliary components or optimize the performance of your dual core or multi core processors, or view the status of everything that’s on your main PCB.
In short, the BIOS system is your window and control panel for the motherboard. And it’s responsible for ensuring that all the aforementioned components are running smoothly and playing nice with one another.
5. CMOS Chip
The CMOS chip has performed this operation for decades and is an integral part of your computer. Everything on your computer gets electricity from the dedicated power supply – except the CMOS, which gets power from a replaceable battery that’s on the motherboard as well.
That is why CMOS stores BIOS settings, its purpose is to retain information when the computer is shut off and so that they do not get lost, including the system clock.
6. VRM Section
VRM stands for Voltage Regulator Module. The VRM is not a single element on the motherboard, but a group of 3 main components i.e MOSFETs, chokes, and capacitors usually located to the left and above the processor socket.
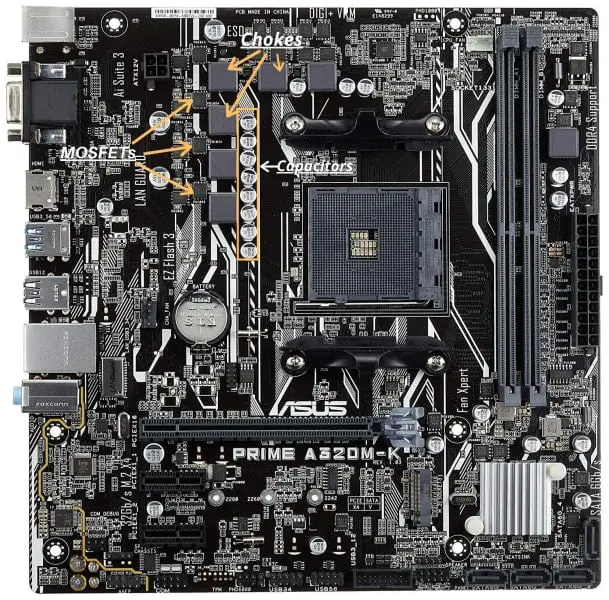

This set of components transform the electrical current that reaches the motherboard into voltages of different values and intensities so that they are used by the other components installed on it.
This component, despite not being particularly conspicuous, is essential for the components to function properly and not cause breakage.
Other Components of Motherboard
On the rest of the motherboard’s surface, you’ll find the slots and connectors for the RAM, graphic cards, hard drives, power supply, cooling fan, keyboard, mouse. For Internet sometimes inbuilt Wi-Fi on the board, otherwise only ethernet port. Other like microphone jack, VGA, sound, and display ports which you can see in the below image.
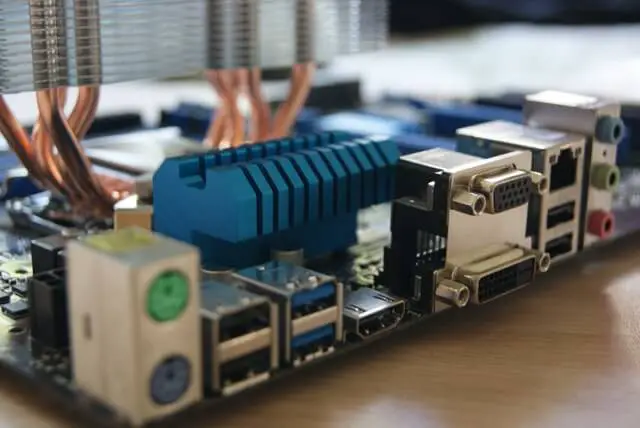

To call a motherboard complex would be a massive understatement. Everything you see on the surface of this PCB has a specific function. This includes the ideal placement of components and connectors on the board.
Even the zigzagging lines on a motherboard are there to balance electric signals and minimize interference.
In fact, modern motherboards are products of decades of development in PCB design systems. Through the collaborative work of PCB engineers and manufacturers, the physical designs of next-gen motherboards continue to get faster and more efficient at facilitating data flow.
Points to be Noted while Building a New PC
Now you know what is a motherboard but what If you’re building a PC from scratch, it’s arguably more important to consider compatibility from the motherboard’s perspective – especially if you’re on a budget.
Currently, MicroATX and ATX are the most common size and layout standards for most modern motherboards. And either is compatible with a large number of removable components, RAM cards, ports, hard drives, CPUs, GPUs, and external devices.
These are just some of the key and fundamental facts you need to know about your motherboard. Keep these facts in mind as they will come in handy when you’re building a new computer or after upgrading your parts, or troubleshooting your PC’s hardware.
If you can keep your motherboard healthy and running efficiently, you can maximize your computer’s performance and prolong the service life of all essential parts.
FAQs
The given are the some of the faqs on ‘What is a Motherboard?’.
What is a motherboard for?
A motherboard serves to connect a multitude of components together and form a useful electronic device. In the field of computers, the rest of the internal components are connected to the motherboard through various connectors and ports. In this way, they are all communicated through the same common element, motherboard.
What is the purpose of a motherboard?
The main purpose of the motherboard is to unite all the components of the computer with each other. It is responsible for allowing the CPU to control the operation of other parts of the computer. That is, the motherboard not only turns all PC components into one whole but also maintains communication between them.
If the CPU is the brain then the motherboard is?
Technically, If the CPU is the computer’s brain, then the motherboard is the spine that connects the brain to the rest of the body.
Is there any full form has for motherboard?
No, there is no full form of Motherboard since the word Motherboard is made of two separate words Mother and Board.
What is a motherboard made out of?
The base of the motherboard is made of a very hard non-conductive material. Since it is non-conductive, it does not conduct electricity. A thin layer of copper or aluminum foil called a wire is printed on the printed wiring board. These wires are very narrow and make up the electrical circuit between the various parts. In addition, it has sockets and slots for connecting other parts.
Is motherboard responsible for transferring the image to the monitor?
The motherboard is responsible for transferring the image to the monitor (if a graphics card is integrated into it).
Do motherboards come with processors or RAMs?
No, the motherboard doesn’t have inbuilt processors and RAMs. In fact, the motherboard comes with ports and sockets which are used for connecting the RAM and processor.
A motherboard is a complex device that connects all the components of a Digital Computer, controls its operation, and determines the amount of equipment connected to a PC. This board determines the characteristics of your PC and sets the limits for upgrading it.
I really hope that the comprehensive article “What is a Motherboard?” is useful to you. Do not forget to share the article on social networks!




