We see many Computers nearby, But they all are different from each other. In this article, we are going to know about the basics and classification of computers which included all the different types of computers.
There are different classes of computer technology available these days. The functionality and data processing of each type of computer is different and output results as well.
However, the methods or techniques, Size, capacity, characteristics, and data handling of the data of each computer may be different too. Let’s Get to Know the “What are the Classifications of Computers System“:-
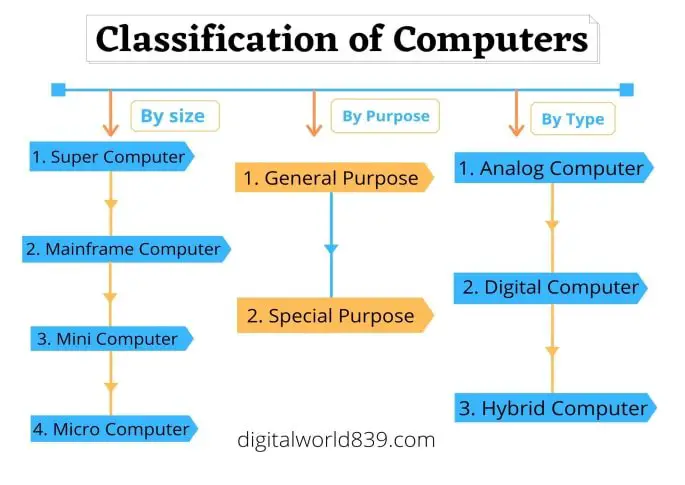
Classification of Computers
We can classify the computers into the following 3 categories:
Classifications of Computers System:-
- On the Basis of Size and Capacity, [Supercomputer, Mainframe, Mini, and Micro Computer].
- On the Basis of Purposes, [General and Special Purpose].
- On the Basis of Hardware Design and Type [Analog, Digital, and Hybrid Computer].
Computers on the Basis of Size and Capacity
1. SuperComputer
A Supercomputer is the very fastest and powerful, and expensive type of computer for processing data. Supercomputers’ size and storage capacity are also huge (can occupy huge premises) designed to process vast amounts of data in a short time with high productivity.
These are specially made to perform multi-specific tasks. Therefore, many CPUs work in parallel order on these supercomputers. This function of a Supercomputer is called Multiprocessing or Parallel Processing.
A supercomputer’s design is complicated, like it can be heterogeneous, combining computers of different architectures, is significantly surpassed most existing personal computers. This made this machine an ultra-high-performance supercomputer.
Each part of a supercomputer is responsible for its own specific task, such as structuring and solving the most complex problems requiring an incredible amount of calculations.

Applications: The uses of supercomputers are dedicated to –
- In research and study of energy and nuclear weapons and designing the aircraft, airplanes, and flight simulators.
- Climate research and Weather Forecasting and Prediction of Natural Disasters.
- Spaceship and Satellite Launching.
- Used in scientific research laboratories.
- Used in Chemical and Biological research and for highly calculation complex tasks.
Examples: IBM Roadburner, IBM Blue Gene, Intel ASI Red. PARAM-1000, and CRAY-XMP-14.
Good to Know ~ World’s first supercomputer is the Control Data Corporation (CDC) 6600 invented by Seymour Cray.
2. Mainframe Computer
Mainframe computers are multi-programming, high-performance computers, and multi-user, which means they can handle the workload of more than 100 users at a time on the computer.
The storage capacity of the mainframe is enormous, with a high-speed data process as well. As well as handling hundreds of input and output devices at a time.
The mainframe is a highly efficient computer capable of simultaneously solving complex calculations and continuously for a long time. These computers have several microprocessors that have the ability to function the data at too high performance and speed.
The mainframe is ahead of our conventional modern Personal computers in almost every metric. The possibility of their “hot” replacement in the mainframe computer ensures continuity of operation. And the standard amount of processor utilization effortlessly exceeds 85% of the total power.
Somehow mainframes can be more powerful than supercomputers because the mainframe supports many processes simultaneously. On the other hand, supercomputers can run a single program but faster than a mainframe. In the past, Mainframes requires entire rooms or even floors of whole buildings for set up.
In today, IBM company is leading the production of mainframe computers. Mainframe reliability is increased with development in the past 60 years. These computers can fix most of the hardware and software bugs.

Applications: Uses of Mainframe Computer –
Mainframe computers are mainly used by departmental and commercial organizations like Banks, Companies, Scientific research centers, and governmental departments like railways. These computers can work for 24 hours. Hundreds of users can work on these computations simultaneously.
Using the mainframe completes the tasks, Such as keeping details of payments, research centres, advertising, sending bills and notices, paying employees, ticket booking, maintaining details of purchases by users, keeping detailed tax details, etc.
Examples: IBM Es000 series, ICL39 Series, and CDC 6600.
3. Mini Computer
Minicomputer is a digital and multi-user computer system with the connection of more than one CPU. Thus, many people can work on these computers simultaneously instead of a single person. Also, it can process with other accessories like a printer, plotter, etc.
Minicomputers are the medium type of computers that have more functionality power and are expensive than microcomputers. On the other hand, the size, storage, and speed of minicomputers are large but less than the mainframe and supercomputers.
Minicomputers are made for performing multiple computing tasks at a single point of time, instead of assigning many microcomputers for a single task, which will be time-consuming and expensive.
In general, a minicomputer is a multi-threaded system (several processes at a time) capable of supporting from one to up to 200 users simultaneously: these computers are currently used to store large databases, multi-user applications, and the automation industry.

Applications: The uses of Minicomputers –
The minicomputers are used as real-time applications in Industries, bookings, and Research Centres. Banks also use minicomputers for preparing payroll for employees’ salaries, records, tracking of financial accounts, etc. As well as in the field of Higher Education and Engineering.
Examples: PDP 11 and IBM (8000 Series).
Good to Know ~ PDP-1 was the world’s first minicomputer, small and interactive, introduced in 1960 by the Digital Equipment Corporation.
4. Micro Computer
Today we are using many computers at home is also the most common microcomputer. With this invention of the microprocessors in the year 1970, it became possible to use computers for people personally at a low cost and reasonable price known as Digital Personal Computer.
The design of microcomputers is minimal in size and storage capacity. These computers consist of many parts like Input and Output devices, Software, operating systems, networks, and Servers all these need to connect to form a complete Personal Digital Computer.
There is not only a PC or laptop are examples of microcomputers. Other examples of the microcomputer are smartphone, Tablet, PDA, server, palmtop, and workstation.
This can be installed in any work area or even at home for personal use.
The primary purpose of microcomputers is to keep and process the everyday tasks and needs of the people. Only one person can work on a single PC at a time, but its operating system is multitasking. The PC can be connected to the Internet to take benefits and enhance the user experience.
The development of multimedia, small equipment, optimized energy consumption, and the LAN made the microcomputers increase in demand for every field.
The increase in the demand and need for microcomputers between the people leads to the tremendous development of each part related to the microcomputers.

Applications: The uses of MicroComputer –
PC is being widely used in many fields like home, office, data collection, business, education, entertainment, publishing, etc.
It keeps the details and prepares letters for correspondence in small businesses, creating bills, accounting, word processing, and operation of the filing systems in a large company.
Some of the major PC manufacturers are IBM, Lenovo, Apple, HCL, HP, etc.
Examples: Desktops, tablets, smartphones, and Laptops.
The fast development of microcomputers with technology. As a result, today, microcomputers coming in the form of a book, a phone, and even a clock in the name of a digital clock.
The above is the classification of computers according to Size and Capacity!
Computers on the Basis Purpose
1. General Purpose
General computers can do various everyday tasks such as writing a word processing letter, Document preparation, recording, financial analysis, Printing documents, creating databases, and calculations with accuracy and consistency.
The size, storage capacity, and cost of such computers are mainly less. The ability of these computers is limited in performing specialized tasks. Still, it has versatility and useful for serving people’s basic needs at home or in the workplace in the environment.
Examples:
Desktops, laptops, smartphones, and tablets are used on daily basis for general purposes.
2. Special Purpose
These computers are designed to perform a particular or specialized task. The size, storage capacity, and cost of such computers mainly depend on the nature and size of the work. The function of these computers is consistent with any particular task.
The special computer needs specific and input and devices as well as a compatible motherboard with the processor to conduct work efficiently.
These computers are used for special purposes in weather forecasting, space research, agriculture, engineering, meteorology, satellite operation, traffic control, and research in chemical sciences.
Examples:
- Automatic teller machines (ATM),
- Washing machines,
- Surveillance equipment,
- Weather-forecasting simulators,
- Traffic-control computers,
- Defense-oriented applications,
- Oil-exploration systems,
- Military planes controlling computers.
The above is the classification of computers according to Purpose!
Computers on the Basis of Hardware Design and Data Handling.
1. Analog Computer
An analog computer performs tasks using continuous data (the physical amount that changes continuously). Analog computers are used primarily to measure physical units like the voltage, pressure, electric current, temperature, and convert them into digits.
It is also used to measure and perform arithmetic calculations of numbers, the length of an object, or the amount of voltage that passes through a point in an electrical circuit. Analog computers obtain all their data from some measurement way.
Analog computers are mainly used in the fields of science and engineering. Analog computers are slow and equipped to measure things rather than countable or check.
The efficiency of this computer increases when we get the result of the data in graphs, etc. Analog Computers cannot store statistics.

They are used in the fields of technology, science, research, engineering, etc. Because quantities like voltage, pressure, electric current, temperature are used more in these areas, these types of computers give only approximate estimates.
Examples:
An analog computer installed on a petrol pump measures the amount of petrol coming out of the pump and appears in liters. And calculates its value. These quantities vary continuously while measuring the amount, such as the temperature of a human body changes consistently.
A simple clock, the vehicle’s speedometer, Voltmeter, etc. are examples of analog computing.
2. Digital Computer
As its name suggests, a digital computer represents the digital computer’s letters, numerical values, or any other special symbols. This computer is the computer that calculates the number for processing the data.
They run on electronic signs, and the binary numeral method Binary System 0 or 1 is used for calculation. Their speed is fast.
It can perform arithmetic operations such as addition, occurrence, subtraction, multiplication, or division and all types of logical(mathematical) operations. Today, most of the computers available in the market are digital computers.
Digital computers are built to bring the solution of equations to an almost unlimited precision, but in a bit slow manner compared to analog computers. To some extent, they all have similar components for receiving, processing, sorting, and transmitting data and use a relatively small number of essential functions to perform their tasks.
Digital computers use discrete electrical signals for operation rather than continuous electrical signals as analog computers have, making them the most common form of computers today because of their versatility, speed, and power.
The desktop or Laptop at our home is one the common and best example of a digital computer.

Other Examples of Digital Computers
- Personal Desktop Computers,
- Calculators,
- Laptops, Smartphones, and Tablets,
- Chromebooks,
- Digital watch,
- Accounting machines,
- Workstations,
- Digital clock, etc.
3. Hybrid Computer
A hybrid computer is a combined complex computer unit built using both analog and digital properties and united by a single control system. The purpose of designing hybrid computers is to provide functions and features that can be found on both analog and digital devices.
The aim behind creating a hybrid computer is to create a kind of work unit that offers the best of both types of computers. Hybrid computers are extremely fast when driving equations, even when those calculations are incredibly complex.
As both the properties of a computer consist in the form of a single hybrid computer made possible to solve too complex calculations or problems, at the same time, these devices are not only too expensive but also able to solve complex issues a bit fastly.
Incorporating the properties of both(analog and digital) computers into hybrid computers makes it possible to resolve more difficult equations immediately.
The analog computer systems solve the equation process immediately. But it is not necessary that those solutions would be completely accurate.
Here, the digital computer system gives 100 % correct solutions, but it takes a bit of time in the calculation. Therefore, Hybrid computers are made to overcome the flaws of both these analog and digital systems.
Applications of hybrid Computer:
Hybrid computers are most commonly used in vast industries, research centres, organizations, and manufacturing firms (where many equations need to be solved).
Also, the solutions and uses of hybrid computers have proved to be much more detailed, accurate, and useful. Hybrid computers are used in scientific calculations, for nations’ defence and radar systems as well.
Examples:
Auto Gasoline pump is the example of a hybrid computer, this device is installed on a petrol pump do not only to measure the amount of petrol but also to calculates its value, in this way It is capable of both functions i.e hybrid function.
The above is the classification of computers according to type and hardware design!
FAQs
What are the three classes of computer?
One can classify the computer system in the following three classes: 1. Computers on the Basis of Size and Capacity include Super, Mainframe, Mini, and Micro Computer. 2. Computers on the Basis of Purposes include General purpose and Special Purpose. 3. Computers on the Basis of Hardware Design and Data Handling include Analog, Digital, and HybridComputer.
What are the categories of computer?
The computers are categorized as Supercomputers, Mainframe computers, Minicomputers, Personal computers, Mobile computers, Laptops computers, Tablet computers, Portable computers, Personal digital assistants, Calculators, Handheld game consoles, Information appliances, Embedded systems.
What are the 2 types of computer?
There are two types of computers; 1. General purpose and 2. Special purpose computers. General computers perform common tasks such as a word processing letter, recording, financial analysis, Printing documents, calculations with accuracy, and consistency. While special computers are designed to perform specialized tasks efficiently in specialized fields like weather forecasting, space research, agriculture, engineering, meteorology, satellite operation, traffic control, and research in chemical sciences.
What are the classification of computers by size?
There are four types in the classifications of the computer by size are Supercomputer, Mainframe computer, Minicomputer, and Micro Computer.
What are the classification of computer according to speed?
The following are the classification of computers according to speed from fastest to lowest: Supercomputers, Mainframe computers, Minicomputers, and personal computers.
What are the classifications of computers according to function?
There are four types in the classifications of computers by function viz. Analog, Digital, and Hybrid Computer. Analog computers are mainly used to measure physical units like voltage, pressure, electric current, temperature. And Digital Computer represents and calculates the digital letters, numerical values, or any other special symbols for processing the data. While hybrid Computer is a combined complex computer of both the properties of analog and digital and united by a single control system.
The above is the classification of computers according to size, capacity, purpose, and functionality. Share the above-given knowledge on the classification of computers on social networks.





Meter installed on fuel stations by which we use to monitor amount and litre is which of computer is it analog, digital or hybrid?
Hi Ishtiyaq, A fuel meter is an analog computer because it is used to measure the quantity of fluid that has been moved during the transfer process. Also, it hasn’t involved any digital data processor, and the binary numeral method used either, so it is not a digital computer but an analog machine.
Wow, it is readable and explicit. I love ❤️ it
Wow! What a great article
You’re welcome, Jeffa.
That’s quite broad i like that
The notes was very easy to understand thanks a lot.
I can understand very well
Wow! Thanks for this productive and resourceful piece of information.
You deserve a thumbs up.
wow very easily explain . think you for your information .
I love the explanation
The information given here is very vital resource