POST is the often necessary part of the booting process of any digital computer, stands for Power on Self Test, and the hardware carries out every time itself, with no human interaction required.
The POST is designed to know whether the motherboard functions and acts typically for each device built into it when the computer is turned on, which is the reason for the second delay before loading the operating system.
If the computer fails the tests by POST, it’s unable to continue further by displaying an error code. This blog gives you a clear idea of what POST is, and its role explained in an easy way. So,
What is POST (Power on Self Test) in computers? What does it do?
The Power On Self Test, or POST, is a diagnostic procedure that a computer performs when it boots up and is stored in the ROM BIOS on the motherboard.
Once the computer is switched on, POST begins to test the hardware of your PC that carries out a series of processes associated with the BIOS to ensure that your PC devices are working well. Whether on a MAC or a Windows computer, the POST is done every time the system is turned on or restarted.
During the POST diagnostics, it stops the machine if any malfunction is detected with your motherboard, RAM, hard drive, video card, sound card, and other input and output devices of the computer. Then a beep sound or a message will display on the user’s monitor screen warning about the fault, which is used to figure out the cause of its occurrence.
POST errors are often displayed in the Bios information as codes, such as “08” for faulty memory, or as a system message, such as “System RAM failed to scroll.” On Mac, POST errors are often shown by a simple graphic, such as a broken folder icon that indicates no boot device was found.
These details are helpful to determine whether your system is operating correctly and what needs to be fixed. That is why you observe a second of pause before the operating system loads. Although these tests are performed quickly, they are still not as thorough as testing a computer with the help of special diagnostic programs.
In contrast, if all tests pass, the rest of the boot process turns on the OS to use the computer. That’ why it is suggested to checking POST is the first step when building a new PC.
What is tests being done by the POST process?
When the computer is activated, the POST executes:
Using POST to recognize failures
The POST procedure provides three ways to convey a problem:
- Beeps sound
- Messages displayed on the monitor screen
- Hexadecimal error codes issued on the / O port
The error codes are present only if the POST detects a malfunction with any component. These are presented under a wide range of acoustic and visual signals to notify the user of the fault found.
Even though most of these POST error codes in computing are diverse according to the manufacturer of the board, you can find a kind of normalization between the most common errors. Let’s see below:
1. Beep sound signals
With the help of a sound beep, the system notifies you of the errors. To issue sound signals, be sure that the system speaker is connected to the pin on the motherboard and is working perfectly. If this is not the case, you cannot hear the beeps of the test system and determine the type of malfunction.
If any malfunction occurs during POST, the program will issue a sound signal (a sequence of short or long beeps and sometimes a combination) describing the error type. The computer will halt working until the malfunction eliminates.
You should pay attention to the number and duration of these beeps. Because after counting the beeps, look up this beep combination to their corresponding faults, which you find in the motherboard (or computer system) documentation to determine what the beep means.
The sound codes are specific to the different BIOS version and are often different for various BIOSs from the same manufacturer. Therefore, most BIOS test boards come with documentation describing the POST codes for different BIOS versions.
However, you can see some of the standard signals in the below image.
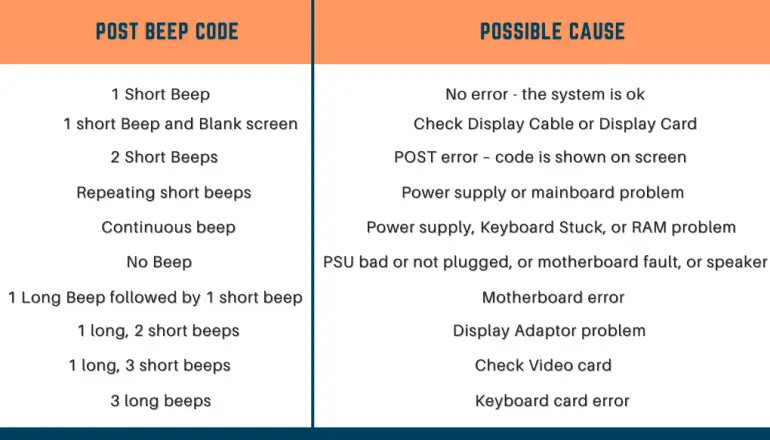
Tip – Sometimes computers generate beep codes when they have encountered some kind of error. The key to determining whether the beep code is an error that’s in the computer’s hardware or something else entirely, at his moment turn on and off the computer three or four times and see if it generates the same beep sound each time. If so, then you are probably looking at a bad hardware situation rather than a faulty power supply symptom.
2. Text messages
POST uses this method besides sound signals if the computer’s video system is working and only after the system loads the video adapter and monitor. A message briefly describing the problem and an error code will appear on the screen.
For instance, in the below image:

By the error code, you can inspect in more detail using the documentation for the motherboard or BIOS. The following are the most common error codes below:
Error Code | Possible Cause |
301 | Indicates the hard drive is failing |
201 or 203 | Memory module failure detected |
1101 | |
601 | Battery error or dead |
161 | Irregular entries in the Windows registry or in configured system |
Note – It is essential to mention that these error codes are different for each motherboard or component manufacturer. There is regularly a significant disparity between them; So what corresponds is to look at the manual of the component to understand each of the error codes of the computer post.
3. Hexadecimal codes via Post Card
Along with the sound or text messages, one can also uses this method. To read hexadecimal codes, you need special equipment installed in the expansion slot called a POST card.
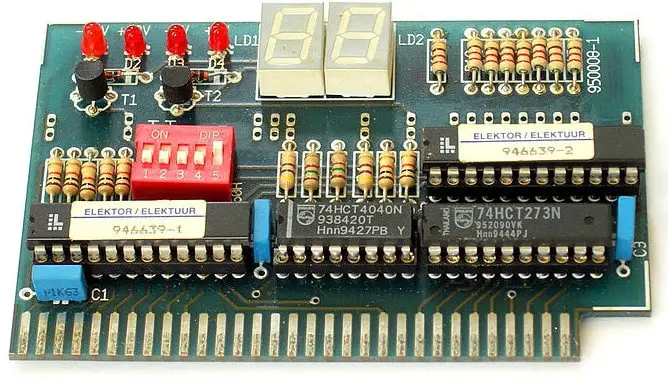
It is initially made for testing motherboards. The purpose of the POST card is to identify possible defects during their manufacture (without the need to connect a video adapter and monitor to them). Now some companies have produced such boards for specialists involved in computer service.
Choosing a POST card is important and should not be approached lightly. There are three bases on which most POST cards are made: the ISA slot, PCI, and AGP. Make sure that whatever POST card you are considering will work with any machine you want to test it with.
In most cases, ISA and AGP cards only work with x86-based computers or PCs; PCI cards may work with either the x86 or other sockets, including those for Power PC use.
Thirdly, far from all users have the POST card required to determine the malfunction, yet sound signals and POST text messages often resolve errors.
Standard steps to resolve errors
If you’re getting some sort of error in the POST code, you can try the following suggestions and look at if they help you resolve the issue before you thought for sending PC for repair:
- Restart
- Unplug any drives or USB devices.
- Disconnect external devices.
- Reconnect the power supply cables.
- Identify the beep code using the component or device manual.
- Check the fans for turned off or on.
- Disconnect all expansion cards.
- Power off and on the computer.
- Check if the BIOS chip is loose.
- Update BIOS.
- Change motherboard, GPU, RAM, PSU, storage disks as a proxy to see whether the POST continues to proceed further.
These recommendations are in no particular order. I recommend trying each one and then checking if the system boots. Likewise, to carry out some of these actions, you may need the services of a hardware technician.
Wrapping Up
POST is quite a technical term that IT technicians only use on a regular basis. However, it is good to know as it will help you better understand error messages that may appear on computers or other electronic devices.
If your computer doesn’t boot due to a POST error, you can use a different device to look up the meaning and cause of the error, possibly from the manufacturer’s website. Then you can take the appropriate measures, as said.
Now, here the article ends “What is POST (power on self test)?” You can share this insights on social networks.