SSD vs HDD Reliability: It is usually believed that SSDs are more reliable than HDDs because they have no moving parts, so they are more resistant to failure due to shocks or impacts, etc., and therefore a more reliable option. However, that’s not the whole story.
You might not know it, but HDDs might be as reliable as an SSD or even more subject to different scenarios. Even so, quite a few factors make SSDs significantly more durable.
In this post, I uncover different aspects of the SSD vs HDD reliability and will also look at statistics on which one is more durable and long-lasting.
HDD vs SDD Reliability
What Makes SSDs More Reliable?

1. No Mechanical Components
Not having any moving parts is the first and foremost reason that makes SSDs tough and long-lasting. With hard drives, a simple fall on the floor might be all it takes to say goodbye to them – because they’re almost dead.
Instead SSDs are based on flash memory chips with a control controller and no moving parts at all, which makes them resistant to shock and vibrations, so you don’t have to be careful about dropping them. That’s actually what makes them more durable than HDDs.
2. TRIM and Wear Leveling
TRIM and Wear Leveling is a new optimization technique installed in SSDs to improve durability and keep their cells from wearing out. TRIM informs the SSD which data blocks it can erase because they are no longer used. This will make the blocks immediately available for the next write session while also preserving the data blocks while unused.
On the other hand, Wear Levelling spreads out the read and writes over all the SSD cells instead of hitting the same cells repeatedly. This even spread of data distribution prevents concentration on a single cell. And thus, preventing wearing out of small parts of SSD would render the entire equipment unusable.
3. Portable and Energy Efficient
SSDs are portable in the sense that their size is smaller, and because they don’t rotate, they are lighter and, at the same time, quieter than traditional drives.
Moreover, a SSD is far more energy efficient as it don’t consume power while they are not being written to. On the other hand, HDDs continuously to take electricity from modular power supply due to the spinning of the hard disks all the time.
For example, M.2 SSDs, their relatively small size and low power consumption, it’s easy to see why they’re ideal for laptop computers as well as the microcomputers like tablets, mobile devices.
How Long Do SSDs Last?
A Solid State Drive can last for at least four to ten years. The first reason is that every SSD are made of NAND flash memory, similar to what you would find in a USB drive.
Flash memory hasn’t spinning parts, so it is not prone to the same failures that mechanical hard drives are. Second, SSDs use wears levelling to randomise their memory chips’ wear. Over time, the memory chips will be worn down to the same level, and there will be no difference.
Because of their excellent reliability, solid-state drives will last for much longer than a standard hard drive yet have a finite number of write or erase cycles. Yes, it means a limited lifetime.
There can be two reasons for the decline in the reliability of an SSD:
Thus, If you use your computer to the maximum every day, the SSD will have to be replaced after 2-3 years. At low loads, the drive will last up to 8-15 years.
How Hard Drives Work and How Reliable it is?
The HDDs have a platter, or disk, which spins around at several RPMs. The disks hold the storage, and the arm reads or writes data. It works like a speedy record player – yes, just like the one you might have seen in your grandpa’s house.
Hard drives have no restrictions on the amount of recorded data theoretically, they can work indefinitely. In reality, everything depends on the resource of mechanical parts: from 5 to 10 years.
What makes HDDs less durable?
HDDs are equipped with fragile and high-precision moving parts, so they are more sensitive to physical damage via shocks or drops. Ironically, you can get away with dropping your $800 iPhone but not your $80 hard drive.
However, desktop systems do not fall to the floor so often. Much less pleasant is the probability of the appearance of bad sectors or the destruction of the magnetic layer of the plates, from which is not immune. Also, in a case of portable hard drive or just for storing use, there is always probable to fall down.
In the worst-case scenario, the arm can irrevocably hit the plates and damage the disks. Hence, reducing the durability of the hard drives.
In addition, HDDs are more sensitive to heat, which becomes an issue at data centers and servers – where they produce quite a bit of heat.
Another factor affecting reliability is the presence of magnets. Hard drives use magnetic storage and are therefore prone to damage or data corruption in close proximity to powerful magnets. Solid state drives are not at risk of such magnetic distortion.
How HDDs Can Be More Reliable Than SSDs?

As mentioned earlier, long-term storage is not suitable for SSDs. So, this is where HDDs shine. Furthermore, SSDs can fail more quickly simply because of their write/erase cycle limitations if you churn through much data in a single day.
Server computers use hard drives mainly for the above reasons, where as high as 1.2 Petabytes of storage can be achieved. That too, on a single machine via hard drives.
Thus, if you need speed, then the SSDs are unbeatable, but if you just need to store files, HDDs do the job much better.
In addition, a study given by BackBlaze also shows that SSDs and HDDs have similar failure rates.
SSDs and HDDs Have a Similar Reliability
Backblaze, an online backup storage company, has released a study that shows that both SSDs and HDDs have a similar failure rate. However, there’s more than meets the eye.
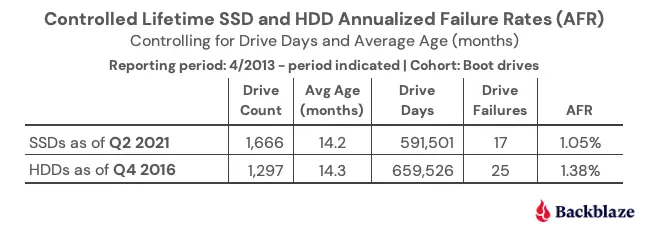
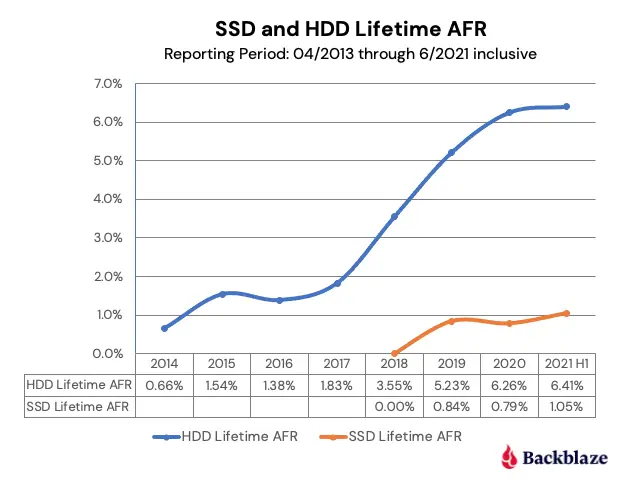
The study between SSD vs HDD reliability is summarized for you below:
Comparing SSD vs HDD Reliability and Conclusion
However, until now, SSD-equipped storage, which has a high unit price per capacity, has not been widely used in the enterprise field. However, the situation is changing drastically as the capacity of SSDs is increasing due to the miniaturization technology of SSDs.
On the other hand, HDDs have a longer lifetime in which they are more reliable, but it doesn’t mean you should go back to replacing your SSDs, which are superior in terms of speed and performance especially the NVMe SSDs.
Yet, more deciding factors to consider are speed, form factor, electricity consumption of PC, other requirements, etc. to suit your needs.
For instance, if we put an SSD vs HDD side by side under a similar workload test for six months, the SSDs would be more reliable. This means HDD would have failed more often, while SSDs wouldn’t have experienced any significant wear and tear.
But, if we increase the duration to six years instead of six months, now the SSDs would have failed more often. This is primarily due to the flash memory cell degradation.
That said, SSD’s high durability during transportation because of shock resistance. And the sensitive mechanical components of hard drives could break or get irrevocably scratched.
So, in conclusion SSD vs HDD reliability, when it comes to portable storage devices, SSDs are faster and safer also have better overall performance, but HDDs are simply much more reliable over more extended periods.
FAQs
Are HDDs still worth in 2022?
Definitely! They have a better cost per GB and can hold much more space than an SSD. This is probably why many server machines run by several hard drives instead of solid-state drives as a computer application in many businesses. For example, a speedy 500 GB SSD might be similarly priced to a slower 2 TB HDD.
Do SSDs use more or less power than HDDs?
SSDs consume less power than hard drives; the power consumption is typically in the ratio of 2:3. This means if your laptop can run for 2 hours on a hard drive, it would run 3 hours on an SSD. Furthermore, an SSD – being faster – would complete a task quicker, therefore consuming high power but only for a short duration.
Why are solid-state drives aren't reliable for archival purposes?
SSDs aren’t as reliable for archival purposes because they need to be turned on to retain their data after a while every time. An SSD stores data as tiny, trapped electrical charges. These electrical charges leak out of their cells very slowly but surely. Therefore, the SSD needs to be used regularly to replenish its electrical charges after some time.
Do SSDs get slower over time?
SSDs, even at their slowest speeds, are still faster than hard drives. However, they do, in fact, slow down over time. To be more precise, they slow down as you fill them up. The simple reason for this is that it doesn’t have any blank sectors left where it can write due to Wear Leveling. You should keep around 25% of free SSD space to prevent it from slowing down as a good practice.
Are SSDs or HDDs better for gamers?
SSDs are kind of the standard now for gamers, especially since PlayStation 5. Your games will load quicker, and as you move across larger maps, the textures are immediately loaded, which could take 1 or 2 seconds and be somewhat noticeable if you’re using a slower hard drive.
Why do people still use hard disks instead of solid-state drives?
There are many reasons people still use hard disks instead of SSDs. They offer an extremely economical cost per GB, which is particularly useful when you need storage in Terabytes – not uncommon for scientific research labs. Furthermore, they have a longer life and are more suitable for archival purposes than SSDs.
This ends our article on SSD vs HDD Reliability. You can leave a comment if you have any suggestions or something to add. Remember to share it on social networks so that it can help more users who need it.