When you purchased your SSD drive, you were probably looking for some tips on how best to take care of this type of drive. Articles often mention the need to leave disk space because this affects the performance of the entire device.
But why this is important and exactly how much space should be left free on the drive is not mentioned so often, and if there are descriptions, they are rather vague.
Therefore, I’ll try to clarify further and tell you how much space to leave free on the SSD.
Why do you need free space on an SSD? What is the importance?
When it comes to maintaining my SSD, I’ve always prioritized ensuring there’s ample space available. The reasons are beyond just having room for new downloads or system updates. I’ve revealed key insights that highlight how critical unused space is for an SSD’s wellness.

For a real-life illustration, look at a recent experiment conducted on the Western Digital WD Black SN770M SSD, published by Xda-developers.
With only 10% of its space filled, the SSD showcased blazing speeds of 4,800MB/s. However, when the drive was 90% full, a drastic drop to 1,200MB/s was observed. This is nearly four times slower, underscoring the dramatic impact that free space can have on SSD performance.
SSD Capacity Utilization | Read/Write Speed |
10% Filled | 4,800MB/s |
90% Filled | 1,200MB/s |
The above table describes how SSD performance is closely tied to the availability of unallocated space. So, let’s know the reasons behind this slowdown and what consequences happen to SSD when you fill it all up.
The Impact of Filling Up Your SSD on Performance
1. Trim Command Struggles
SSDs rely on TRIM technology to manage data, which efficiently clears blocks of data that are no longer in use and ready for rewriting. When an SSD is near capacity, TRIM struggles to perform efficiently because it has to spend more time finding available spaces to write new data; this not only slows down the process but can also affect the life of your drive.
This degradation is not immediately noticeable, but over time, it can significantly drop your SSD’s speed and responsiveness.
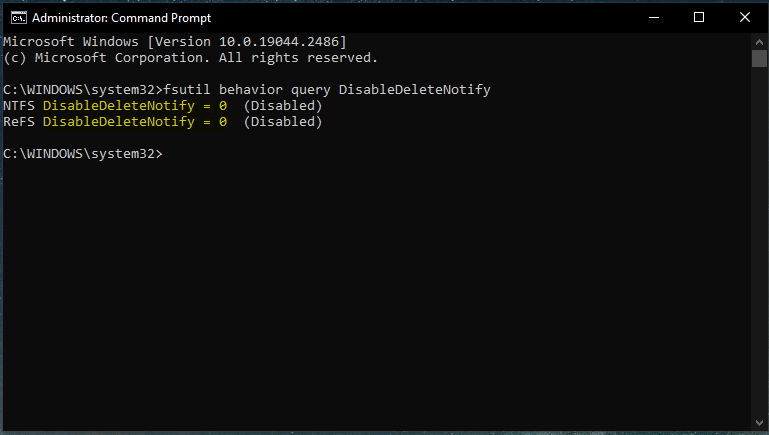
To check if Trim feature is enables in your device: Run CMD as administrator and type or copy paste this: ‘fsutil behavior query DisableDeleteNotify’ and press enter. TRIM is enabled if the cmd shows the result for NTFS and ReFS: DisableDeleteNotify = 0 (as shown in below image)
2. Wear leveling process
Wear leveling is another important concept to understand. It refers to extending the life of your SSD drive by distributing write and erase cycles across the memory chips evenly to prevent certain areas of the drive from being overused and worn out prematurely.
The logic behind this is rooted in the way SSDs work. Each time data is written to or erased from an SSD, it slightly degrades the memory cells it uses. Plus, SSDs are designed to handle a finite (limited) number of these cycles before the cells become unreliable. Distributing data evenly across the drive’s cells minimizes premature wear on any single part of the SSD.
A well-implemented wear-leveling mechanism can significantly extend the lifespan of an SSD. If an SSD storage is almost complete, it becomes less effective, causing some cells to wear out faster than others. This imbalance can shorten the lifespan of solid-state drives.
Thus, with more free drive space, the SSD controller can distribute write and erase cycles across a broader range of cells (MLC or TLC), which minimizes wear and tear on the drive over time.
3. Reduced Read and Write Speeds
When an SSD approaches its total capacity, the efficiency of both read and write operations begins to deteriorate as it requires a certain amount of free space to perform operations efficiently. While read speed is not as noticeable as the write speed reductions, it can still affect overall system responsiveness and application loading times.
To give you an idea of how severe this impact can be, I’ve compiled some data on SSD performance as it relates to unused space:
Free Space Left on SSD | Approximate Reduction in Write Speed |
10% | up to 5x slower |
5% | up to 10x slower |
This data illustrates why leaving adequate unused space on an SSD is more than just a good approach.
4. Garbage Collection
Apart from wear-leveling, garbage collection also plays a critical role in the longevity and performance of SSDs.
SSDs store data in blocks, and when files are deleted, these blocks don’t automatically free up. Instead, they are marked as available, yet they still contain data until they are overwritten. This is where garbage collection comes in.
It’s a background process that clears blocks marked as available to ensure that when new data needs to be written, there are empty blocks ready. And yes, garbage collection can also perform optimally only when there’s sufficient free space on the SSD. Without enough free space, the process becomes sluggish, affecting overall SSD performance.
5. Impact on Operating System and Application Performance
Leaving a certain percentage of your SSD free influences not only the speed at which your OS operates but also how efficiently your applications run.
For instance, everyday tasks such as booting up your computer or launching programs become noticeably more immediate when your SSD’s storage has ample free space. This speed boost is a result of the SSD controller having the flexibility to access and write to numerous empty blocks quickly.
Let’s not overlook the application performance either. Applications that continuously write and read data from the SSD can lead to a bottleneck effect where the system has to fight through the clutter to find space for new data or to retrieve stored information. This can result in longer load times for applications and even lead to crashes or errors in more extreme cases.
For instance, a Windows system with a filled-up SSD disk will refuse to run troubleshooting programs, displaying a message that clearly tells you, “The problem prevents the launch of the troubleshooting program.” This is a stark reminder of how essential free space is for basic system maintenance and troubleshooting.
6. Effect on SSD Cache
Like traditional hard drive (HDD) uses cache system, similarly, modern SSDs come equipped with a caching mechanism whose efficiency directly correlates with the amount of available free space on your SSD drive.
The principle behind SSD caching is straightforward: it serves as a middleman between your data and the slower parts of your SSD. When your SSD has ample free space, it allows the cache to function at its peak, storing and accessing data with remarkable efficiency.
As the SSD fills up, less room is available for the cache to operate effectively, resulting in a noticeable decline in data retrieval speed and, thus, slower system performance and longer load times for applications and files.
How Much Free Space Should I leave on my SSD?
A guiding principle is always to ensure free space of around 20% on your SSD. This isn’t a random number but a well-considered recommendation that strikes a balance between usability and the drive’s technical needs like wear leveling, garbage collection, trimming command, caching, and other processes.
Experts often quote this range as a sweet spot for maintaining optimal performance while allowing for regular use and data storage.
Here’s a glance at why leaving unused space on SSD drives is vital:
Considerations for different SSD Sizes
When deciding how much free space to leave on my SSD, it’s crucial to consider the size of the drive because the recommendations shift slightly from small to large-sized SSD capacities.
For larger SSDs (1TB and above), leaving about 10% of the drive’s capacity as free space is generally a good rule of thumb. This space is vital for the drive’s wear-leveling, garbage collection, and trimming tasks. For instance, a 2TB SSD would benefit from having 200GB of unused space. This might seem excessive at first glance, but it’s essential for maintaining the drive’s performance and longevity.
However, for smaller SSDs (those under 1TB), especially those hosting Windows, the scenario changes slightly. Windows updates, as I’ve learned from experience, can consume a significant amount of space temporarily. Therefore, for drives under 1TB, it’s wise to ensure at least 25GB to 32GB remains free to manage these updates smoothly. This helps avoid potential system crashes or update loops that can occur when the drive runs out of space during an update process.

In line with solid-state drives, other storage devices like mechanical hard disk drives also need 15 to 20% of free disk space so that Windows can defragment it properly.
Is Leaving free space on SSD Really Necessary?
SSD Manufacturers and Windows recommend reserving some space on an SSD, While it may not be absolutely necessary, it’s a good practice. Modern SSD drives are pretty reliable today; even if you use them up to 95%, they won’t become dramatically slower, yet, performance degradation can occur as time passes.
Still, you should not delay this situation further as it is and free up space on your SSD since the performance of your personal computer decreases significantly as time goes on.
In fact, the issue of free space on SSD drives remains debatable. Therefore, to make sure how much empty space your specific SSD needs, you can also use your personal experience by filling up SSD only up to 95% or more and checking if it is slowing down significantly at your own risk, as it is not suggested.
So, in conclusion, for the question “How much space should I leave on SSD free?” – it is from 10 to 20% depending upon capacity of SSD with no partition.
I’ve thoroughly explored this topic to simplify and ensure that after reading this article, you won’t need to look elsewhere. Remember, optimizing your solid-state drives with free space isn’t just about boosting performance—it’s also about safeguarding your investment in the long run.
I hope this post is insightful for you, and I welcome your opinions and experiences regarding this topic in the comment section.
Related Posts