These terms are two of the most important in the world of fastest storage technology, but what makes them different?
As you may have guessed, both SATA and NVMe are the SSDs. Since there are differences in their performance, some prefer NVMe while others go for SATA most times as per their usage needs.
So it’s essential to understand them before you make a purchase. So, you’ll be able to choose the best option in the market for your PC.
So,
SATA vs NVMe
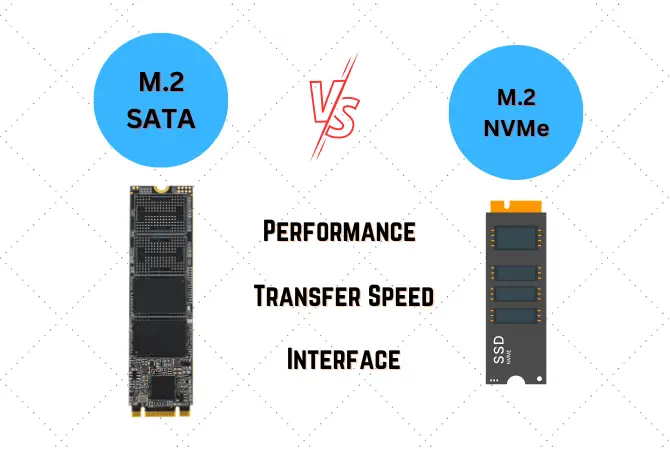
How is NVMe Different from SATA?
In order to properly compare each device, one must have a basic understanding of the differences between storage units. Each storage unit type has its advantages and disadvantages, and it’s important to consider our specific needs, budget, and compatibility.
SSDs are known for their speed but are sometimes limited by the connection type. In this case, even the latest SATA III connection uses traditional hard drives. NVMe is an open standard that allows modern SSDs to perform at the same read/write speeds as flash memory by running directly as an SSD through the PCIe interface rather than being limited to slower speeds for SSD via SATA.
The use of a PCIe interface makes the NVMe provide greater bandwidth and allows for more data to be transferred per second, that can be at least six times higher than SATA SSDs, which provides greater bandwidth and allows for more data to be transferred per second.
It’s worth noting that SATA 3 interface hasn’t changed much since its release in 2008, while PCIe 3.0 from 2010 improved to PCIe 4.0 in 2017 and soon by 2024 we will have PCIe 5.0.
As a rough figure, a SATA SSD has about 550GB/s of speed on average, while PCIe 3.0 and PCIe 4.0 has About 3,500 GB/s and 7,000 GB/s.
One of the big differences is that M.2 SSDs with NVMe make use of low-latency parallel data paths, severely outperforming SATA in performance and latency. In practice, an M.2 SATA SSD can move around 1000-2000 MB/s, while NVMe ones go over 3000 MB/s without problems.
NVMe can support multiple I/O queues (up to 64K), whereas SATA only supports a single queue, and each queue can have between 254 and 32 entries (each NVMe queue has 64K entries). On the other hand, the software gives enough relief to the CPU in data transfers by creating several queues.
So, NVMe is the “next level” because its architecture makes it possible for applications to execute and finish multiple I/O requests at the same time. Not only does it manage to improve speed, but new commands have been added that minimize consumption, which can be extraordinary and ideal for portable equipment.
There is one thing where SATA SSDs win, and that is when it comes to operating temperatures. NVMe SSDs are prone to overheating, which rises very quickly and causes a significant drop in performance. To prevent this, NVMe drives require some heatsink to manage the excess heat and prevent a drop in performance.
SATA vs NVMe – Performance Comparison
1. OS Booting Time
We ran tests on Windows 10 operating system by running some programs at startup, like graphics card drivers and keyboard/mouse software. We installed one on a SATA drive and the other on an NVMe drive. We measured the time it took from pressing the power button to seeing the desktop and being able to use the computer.
We found that booting with the NVMe SSD was 8 seconds faster than with the SATA 3. While this is a significant improvement, it’s still not as big of a difference compared to a mechanical hard drive, which takes over a minute to boot up.
2. Copying Files
To conduct this test, we used a third PCIe NVMe SSD to achieve maximum read speed. Then, we manually transferred a faked 30GB file to both SSDs and compared the time it took. We observed a significant difference in speed, with the NVMe SSD offering triple the performance and taking only one-third of the time compared to the SATA 3 SSD.
Please note that this comparison was on transferring a single, large file. Transfer speeds may differ when transferring multiple smaller files.
3. Game Loading Time
We are conducting a test to determine how long it takes for the game to load a saved file on either SSD. The timing starts from when we click “load game” until the game is fully loaded and ready to play, not from when we first enter the game.
This test is significant as it not only affects loading screens but also impacts the overall performance of the SSD once the game is loaded, except for loading screens.
The NVMe SSD seems faster than SATA, but the actual difference is only slightly over one second, never quite reaching two seconds. Therefore, the difference is negligible.
With all these tests, we have noticed that, in everyday situations and real life usage, although NVMe SSDs indeed provide an extra level of performance, it is not really something very noticeable, so we cannot say that it is “noticeable” too much to use one or another type of SSD.
Although benchmarks show a clear difference, the time savings provided by this extra performance need to be more substantial to justify choosing one type of SSD over another, and we do not believe it is worth the increased cost in any of the cases we have tested.
When to Buy NVMe?
Despite the fact that NVMe offers very little performance improvement in everyday scenarios, Still, you can use NVMe in your computer for applications such as video editing, gaming or graphics design that require fast load times and smooth data processing than having as it could make sense as long as the budget allows.
At last, if speed is the important factor for you, then NVMe is a no-brainer choice. It’s the fastest type of SSD available today and can provide lightning-fast transfer rates for accessing data.
Before purchasing a drive, ensure compatibility. There should be M.2 slot and NVMe support in the motherboard as well as in BIOS (it might be worth updating the BIOS, as NVMe support may be added in more recent versions).
Why SATA is Suitable in Most Scenarios?

SATA SSDs are usually less expensive than NVMe drives and offer plenty of speed for most applications. They may not be as fast as NVMe, but they will still provide a near boost in performance if compared. Also, the price difference between a SATA and M.2 PCIe SSD of the same capacity is minimal.
SATA 1 2 or 3 compatibility is much wider with more systems and motherboards form factors, so if you’re looking to use an older system, you may have more success using a SATA SSD than an NVMe one. In addition, since SATA is the most widely used type of storage, it can often be easier to find compatible drives and parts for repairs or upgrades. This makes them ideal when cost and compatibility are the main considerations.
That said, NVMe offers much more impressive speeds than SATA. Going with an M.2 PCIe SSD will provide a much faster boot up time, file transfers and loading times in games and applications. Additionally, features built into the protocol, like TRIM support, can significantly increase performance over time.
- Related: SSD vs HDD: Which Is More Reliable, Durable & Long Lasting?
- Read Also: HDD vs SSD power Consumption » Differences & Calculations.
Final Words
Overall, regarding speed, features, and reliability, there is no question that NVMe is the superior choice. It offers significantly faster speeds than SATA as well as additional features like TRIM support. This makes it the ideal choice for applications where performance matters more than cost or compatibility.
On the other hand, SATA is still a reliable option due to its widespread availability and compatibility. This makes it a great choice for users looking for an affordable storage solution that is still reliable and fast enough for everyday tasks.