Today I’ll be tackling the nuances of HDD vs SSD power consumption.
Do you ever wish your laptop could last hours longer without needing a charge? Have you considered upgrading your storage drive to efficient one to save power and extend its battery life but needed help figuring out where to start? If so, then you’re in the right place!
In this post, I’ll compare SSD vs HDD power consumption – so that you can make sure you’re making an intelligent decision when selecting the storage drive for your computer. By understanding exactly how much energy each type of disk requires, you can save some cash or electricity bills and maximize performance!
SSD vs HDD Power Consumption
The higher the HDD/SSD power consumption, the higher the electricity bill per hour, especially if you’re using multiple hard drives for data storage. But can you save on your battery life and bill by checking the power consumption and using an HDD/SSD that consumes less power?
HDD vs SSD power consumption can affect your laptop battery life. Knowing the differences between their power requirements can help determine how long your laptop will last with one full charge.
Let’s check the difference in power consumption of HDD and SSD drives installed in the computer.
HDD Power Consumption
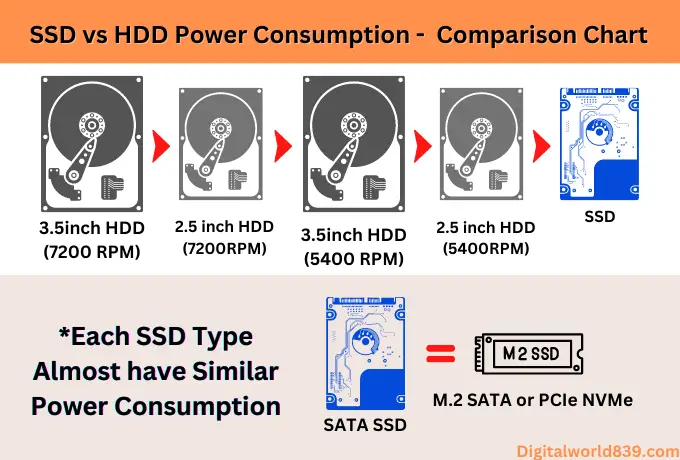
HDDs read and write data using a metal disk that rotates at high speed, and a part called a head, so the motor consumes much power. The internal HDD comes in 3.5 or 2.5-inch widths, and laptop PCs use 2.5-inch HDD widths. Contrary to popular misconception, power consumption does not depend on the drive’s storage size.
A 500 GB, 1 TB, 2 TB, 4 TB, and even 6 TB HDD, if they are of the same brand and from the same line width, will consume the same amount of electrical energy. This indicator is mainly affected by the platter or disk’s speed. So, power consumption will be higher if the recording disk is rotated at high speed to increase the read/write speed.
For example, hard drives with 7200 rpm have more power consumption than 5400 rpm since the electric motor has to make less effort. Currently, “7,200 rpm” and “5,400 rpm” are mainstream.
Note that the power consumption of the HDD will be the highest during reading and writing and decreases when it is not read or written (idle). Also, if there is no reading or writing for an extended time, the disk stops rotating and enters a state (standby/sleep) that consumes almost negligible power.
Well, now the numbers themselves. On average, a hard drive consumes about 4-5 watts in write/read mode and 2-3 in idle mode. Consumption can reach up to 8-15 watts at high usage. Most of the energy in the computer is consumed at the start, during the loading of the operating system.
The 2.5-inch form factor HDD used in a laptop consumes less power: a smaller diameter magnetic disk has less weight, so less effort is required to set it in motion.
HDD Power Consumption
Unlike SSD, HDD has moving parts and a platter that uses more power. SSD records data in memory; it has no moving parts and consumes less energy than HDD.
You should not be considered by the parameters of a conventional hard drive since the power consumption of an SSD is much lower. The power consumption of SSD drives connected via the SATA 1, 2 or 3 interface during recording does not exceed 3.5 watts in write mode and averages 2 watts in read mode. In idle mode, such a device consumes 0.5 watts, and in sleep mode, 0.05-0.1 watts.
In the case of M.2, drives installed on M.2 slot are connected through a different slot, and they are structurally almost the same as SATA storage device. Accordingly, M.2 disks consume the same energy as in the previous case (2.5-inch SATA).
SSD vs HDD Power Consumption > Calculation
Consider that typical SSD power consumption = 0.150*0.2 + 0.1*0.8 = 0.11 W
(20% active usage and 80% passive, hence the SDD power data).
Typical HDD power consumption = 0.05*2.2 + 0.15*1.1 + 0.8*0.8 = 0.915W.
(5% search, 15% work, 80% idle, hence HDD power).
When taking into account typical SSD power consumption, the increase in operating time will be 100/(92+8*0.11/0.915) = 7.57%
So, if your laptop lasts 4 hours on battery, then using an SSD will give you an extra 18 minutes of battery life.
To be more precise, actual work on a laptop will be done in about 20-40 minutes since the SSD works faster, which increases the efficiency of the work itself.
Through careful observation of the numerical values, it can be concluded that there is not a much difference in computer electricity usage bills when leaving the power on for an hour or even if you use it for a whole day, the price difference is less than 1 cent, so it is unlikely that you will leave the power on all the time.
Since the HDD physically rotates the disk, you might think there would be a big difference, but it’s surprisingly significant but a slight difference. Regarding power usage, while PC building thing you can choose without worrying about the power consumption of the HDD. But it doesn’t mean HDD is more reliable than SSD!
- Read Next: SSD vs HDD: Which Is More Reliable, Durable & Long Lasting?
- Related: Can A Power Outage Damage A PC? Or Power Surge Or Both?
FAQs
Which one consumes less power than the other, 5400 rpm or 7200 rpm?
The 5400 rpm HDD is more power efficient and consumes less energy than a 7200 rpm HDD.
Can hard drive power consumption be reduced?
This does not make sense to consider since by reducing the power current; the device will simply stop working.
Is there any difference in power usage of 2.5-inch SATA vs M.2 SATA?
There is no difference in the power consumption of SSDs connected via SATA or M.2 slots. The only difference between them is their size and speed. SSDs with M.2 slot offer faster data transfer speeds than SSDs with SATA ports, but both SSDs consume the same amount of power.
What is better, a laptop with SSD or HDD?
At the level of power consumption, heat and noise, all are advantages for SSDs, which, since they do not have mechanical parts, heat up less than HDDs (particularly concerning “fast” ones such as those of 7,200 rpm and higher), consume less energy and are silent.
Does NVME need more power than HDD?
NMVE SSD drives are connected to the motherboard via the PCI-E bus. Compared to the SATA, they do not have any differences in work and consume energy in the same volumes.
I hope you figure out the ‘SSD vs HDD power consumption‘ leave the comments if you have any question and something to add.