Are you sick and tired of experiencing unwelcome WiFi Interference? Don’t worry. Here, I’ll explain what blocks WiFi signals – like the things. Understanding the root causes of interference can make troubleshooting more accessible and lead to quick fixes in many cases.
There are many situations where hardwiring the Internet to achieve the best internet speeds might be challenging.
For example, when working in an organization where many people frequently bring their laptops in and out and switch rooms connecting Intranet for Internet. Even at home, you might move from room to room or find yourself confined within a small area surrounded by walls – these conditions can prevent reliable signals too.
To know the top five common sources of wireless interference, along with some easy solutions to reclaim your network speeds and optimize your WiFi performance! Let’s begin.
What Can Affect The Quality Of wifi Signals?
When you need strong wifi signals for your daily use, you need to ensure there isn’t anything that can weaken the signal strength; otherwise, your download and upload speed – which is dependent on the signal strength – would be reduced as well.
Wifi produces radio frequency, just like Bluetooth and other appliances within your space. Interference can be caused when something interacts with the wifi signal on the same frequency. Knowing all the leading reasons that block wifi signal strength helps you address them and fix them to get the best possible speeds on your wifi.
So what are those things causing WiFi interference?
1. Walls And Other Solid Objects (because obviously)
Wi-Fi signals are radio waves that travel through the air to transfer information. Hence, it is easily understandable how walls and solid objects can affect their communication.
If you’re experiencing weak Wi-Fi signals in certain areas of your room, it might be due to walls and solid objects in the way. In the case of thick concrete walls and floors, Wi-Fi transmission would be more affected.
Here are some of the interference levels caused by the type of walls in the home.
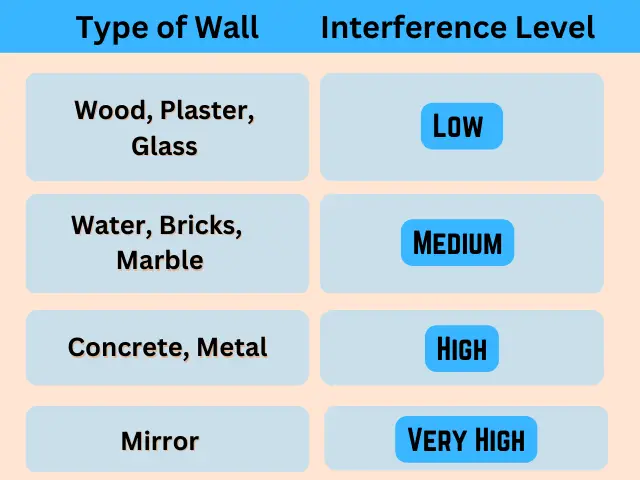
It seems strange, but mirrors cause the highest interferences because the problem with the mirror is the coating applied to the glass to turn it into a mirror; this coating is metallic and absorbs signals in big. If the mirror hangs next to the router, the signal can bounce off the shinier surfaces, deteriorating the signal quality.
It is evident that the dense the walls and have closely packed together, the more difficult it will be not to lose a signal as there is less free space for signals to travel through the medium, such as in the case of Bookshelves – it will be like having built a large signal damper.
Easy Fix
- Changing the walls inside the home is a tricky task, so you can simply avoid working in areas where the walls are prominent.
- Move your router to a central location, free from walls and other obstructions, or else consider getting a range extender to help boost your signal strength in hard-to-reach areas.
2. Electronic Devices (suffering from success)
Your WiFi router is not the only electronic device in your home that emit radio waves with the same frequency. For example, microwave ovens, refrigerators, cordless phones, Bluetooth speakers, Baby Monitors, Walkie-Talkies, etc., emit electromagnetic interference (EMI) to transmit the signal.
As a result, when two competing systems operate on the same RF band at home, RF interference occurs without a doubt due to overlapping signals.
This is especially true when the devices are more than one, and all the signals try to pass through the same frequency, preventing you from utilizing your full wireless bandwidth.
Easy Fix
- First, determine whether the interference is coming from a specific device. You can use an app like WiFi Analyzer for mobile phones to detect sources of interference in your home and then switch off that particular device when not needed or try moving your electronic devices away from your router or turning them off entirely when not in use.
- Most household devices operate on the 2.4 GHz frequency band. Therefore, moving to the 5 GHz frequency band might improve your WiFi signals.
3. Other Wireless Networks (your neighbors don’t live in the stone-age either)
Today, not having the Internet can raise some serious eyebrows, which means your neighbors almost definitely have Internet, reaching your space, which could be the same frequency band as 2.4 GHz.

If too many networks are around your home, your Wi-Fi spectrum might become congested. This issue becomes worse if you live in a dense neighborhood or even in apartment blocks. The more active routers in one place, the more interference experienced.
Easy Fix
- You can talk to your neighbors about setting up their routers at different frequencies from yours, and you can also change to a less congested channel by tweaking the settings in your router. This could help you identify which channel has fewer active routers in the vicinity and thus improve performance.
- Sometimes, creating a guest network with its network name (SSID) on the same router helps as it attracts the majority of the traffic, leaving you with free space for your higher-priority connections.
4. Bluetooth (Wi-Fi isn’t the only thing that’s wireless)
Bluetooth devices, such as Headsets, Keyboards, Mice, Adapters, wireless speakers, etc., are common in homes and offices. They have been identified as sources of RF interference to communicate other computers.

Bluetooth uses frequency hopping technology, which operates on the 2.4 GHz frequency band approximately 1,600 times in a single second! This means that if your Wi-Fi is running on the 2.4 GHz band, you can expect severe turbulences in your Wi-Fi signal when a device pairs with another device via Bluetooth.
In this case, try disconnecting the devices that use Bluetooth technology and see if the connection improves.
Easy Fix
- Switch your wireless router to the 5GHz frequency band, which has more free space than the 2.4GHz band, and leave the 2.4 GHz band for low-priority devices.
- Try using Bluetooth devices based on the Bluetooth specification version 4.0 or later, which uses LE (Low Energy) technology. This technology allows you to limit the amount of affecting Internet speed.
- Move Bluetooth and its pairing devices at a certain distance from your router away from the router and Wi-Fi devices and vice versa.
5. Other Things That Block WiFi Signals at Home
Metal Objects
Metallic surfaces are known to disrupt WiFi signals, whether the metal is thick or thin such as furniture, decorations, or even railings. The metal objects prevent the signal from passing and can also reflect them. Both are equally worse as the former reduces signal strength, and the latter causes wasteful signal overlaps.
Yes, the TV is on this list too. Placing your WiFi router near or behind the TV can be a great idea for home design. However, their internal metallic parts may disturb signal strength coming from the router as an electromagnetic shield. For that reason, it is not advised to place routers right behind, on the TV, or on any furniture made up of metal.
For an easy fix, move your router away from metal objects as much as possible and avoid keeping them between your device and your router or the other way around. A WiFi range extender might also come in handy to fix this problem.
Water
Yes, water blocks all radio waves, including WiFi signals. Placing a router next to ample water storage, such as an aquarium, is like putting a silencer on it. Water absorbs the signals and makes it difficult for them to pass through. The absorption of the signal by water depends liquid density.
Therefore, you can expect spotty WiFi in certain areas if you have an aquarium, water pool, tap water tank, or fish tank.
Place your router away from any water storage source and ensure the WiFi range doesn’t extend to those areas.
Wireless game controllers
Wireless game controllers are portable devices for wireless control of game consoles. Using wireless technology, these game controllers allow players to sit in a room almost anywhere (up to 9 meters away from the game console).
For better coverage, many wireless game controllers operate at 2.4GHz. Like other non-WiFi devices that also work in the 2.4GHz band, wireless game controllers close to an 802.11 WLAN may interfere with regular wireless LAN operation.
Wireless game controllers are available for all major game consoles and computers. Below are some of the major brands:
- Sony PlayStation® Wireless Game Controller
- Microsoft Xbox® Wireless Remote Control
To minimize interference:
- Try maintaining a “safe distance” between the 802.11 access point and the wireless game controller.
- Check your wireless game controller’s working channels to ensure they don’t overlap with the active channels of your 802.11 network.
- If possible, move to the less congested 5GHz band or upgrade your wireless LAN to 802.11ac.
Distance From The Router
This is intuitive as the further you are from the router; the weaker would be the WiFi signals. It decreases over distance, so you don’t get a uniform signal strength in every corner of your house. It is important to note that WiFi signals are directional – they travel in one direction only, so make sure the router is pointed in the right direction.
Keep your router at your house’s highest and central point and install it in an elevated position. Also, make sure that you’re close to the router, as WiFi wireless has a limited range. The best way to do this is simply as easy as moving closer to the router. But if that’s not an option, you can invest in the WiFi range extender.
Some Techniques To Have The Best Possible Wi-Fi Signals At Home
2.4 GHz vs. 5 GHz
2.4 GHz is also known as The Legacy Band, as it has been extensively overused across all wireless LANs for the past ten years. As a result, Bluetooth devices, baby monitors, microwave ovens, garage doors, and many more devices are found on this band.
5 GHz is a relatively newer frequency band supported mainly by newer equipment. It also has a shorter range (although the speed is faster); therefore, devices on this frequency band are less likely to face interference from other 5 GHz networks.
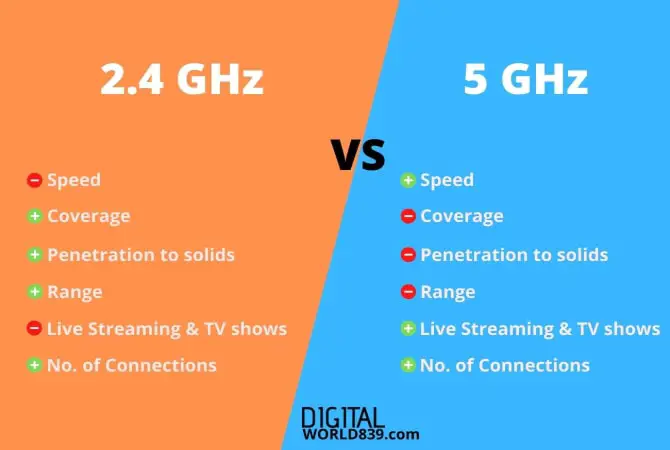
Additionally, the 2.4 GHz band has only 3 non-overlapping channels, but the 5 GHz band, on the other hand, has 25 non-overlapping channels! It is suggested to switch to 5GHz if you have a dual-band router and most of your devices support it.
Channel Width
The wider the channel width, the more data can be sent at a time. However, the wider you make the channel width, the more susceptible it is to interference. So if your router is near other routers or devices using similar channels, you will experience a lot of lag and disruption.
That’s why selecting an optimal channel width is vital according to your network activity and the surrounding environment. Depending on your hardware capability, you can choose from 20 MHz, 40 MHz, 80 MHz, and 160 MHz.
20 MHz – When you have minimal interference, only a few devices are connected.
40 MHz – When you live in an apartment or a densely populated area.
80 MHz – When you have a lot of devices connected, or you’re using them for a connection for gaming.
160 MHz – When you have an extremely high-speed connection with many devices connected.
Position The Router and Antenna Properly
It’s always a good idea to place the router in an elevated position and away from other devices that might be causing interference. Try to keep it as close to the center of your house as possible to get the best coverage.
Also, ensure that the router’s antenna points in different directions. This will help you get a better signal and ensure you don’t face interference from other routers or devices.
Embrace 6 GHz
The 6 GHz band, also known as Wi-Fi 6, is the newer version of the Wi-Fi standard. It offers faster speeds, lower latency, and power efficiency – thanks to Target Wake Time (TWT), which allows devices to schedule when to transmit data.
Wi-Fi 6 is rare technology supported by few devices, offered by even lesser service providers. If you can get your hands on this tech, you are in for an interference-free Wi-Fi experience.
Tools That Can Help Track Down Interference
There are a variety of tools available that can help you track down interference on your WiFi signals. Most of these tools work by generating heat spots as you take a survey across the area of your WiFi network.
You will need the right apps and wireless adapters, such as those offered by NetSpot, AirMagnet, or Ekahau. As you walk around your home, the survey devices will record the data, analyze it, and generate a heatmap. You can view this heatmap and determine good and bad WiFi spots and unearth objects causing obstructions in your WiFi signals.
- Read Also: How To Tell If A Motherboard Has WiFi? (In 5 Easy Steps).
Final Thoughts
Wireless is everywhere, which might sometimes mean some interference that can degrade the wireless signals, particularly the WiFi signals.
Some easy practices can assure good WiFi signals, such as moving your router to an appropriate location or moving the problematic objects to somewhere where they cause minimum interference. Moving to another frequency band help too, from 2.4 to 5 or 5 to 6.
If nothing works, you can try a WiFi range extender. They are readily available from a majority of sellers and suppliers. You can even DIY-build them yourself. After all, you have seen enough WiFi range extenders built from Pringles cans on many tech movies and shows (right, Mr. Robot fans?), so there might be some truth behind them. Spoiler alert: they work!
Thus, by taking the necessary measures and troubleshooting, you can improve your WiFi performance in no time!
This concludes the article “Top 5 Things Causes WiFi Interference (Quick Fix Solutions)?” remember to share it on social networks so that it can help more users who need it.