Smartphones, telephones, printers, TVs, and other devices are connected to the Internet. All this works well within the home network, but it isn’t easy to provide a connection from outside the Internet.
To do this, it is desirable to have a static IP address so as not to suffer from the setting. Today let’s explore the best choice for network connectivity: static or dynamic addresses, their configuration, as well as the advantages and disadvantages.
What is a Static IP address?
A static IP is a permanent address for your equipment on the Internet. It won’t change, no matter what. There are generally two types of address assignments: static and dynamic. The static option is less common due to higher costs for the provider.
On the other hand, dynamic addresses are usually used as they are easier to set up and don’t require extra effort from you or your provider. Let’s look at the pros and cons of using both connection types.
Differences from Dynamic IP address
Imagine explaining this concept using a home router as an analogy. When you set up a router, you configure a DHCP (Dynamic) server that assigns a unique network ID to each device that connects to it.
The server takes addresses from a specific range, like 192.168.0.2 – 192.168.0.255. So, when your smartphone connects, it gets assigned a random free address. It’s interesting to note that this address can differ every time you connect. Pretty convenient system.
It does not require additional settings and works without problems as long as the number of devices on the network is less than the number of addresses. Throughout your session, data packets are sent to this address. If you restart your device, a new internal address is assigned. Rest assured, this address is not shared with the external network.
We figured out the dynamic address, now let’s talk about the permanent one. For example, if you put IP 192.168.0.33 on the computer, it will not accept another one, so finding it on the network will be easy.
This is a static address, it will allow you to configure some specific speed privileges on the router or something like that. You can set up restrictions or relaxations in another way. Just take IP identification as an example.
Scope of a static IP address
When you set up the static IP address option, it is possible to configure a permanent IP to equipment from anywhere, whether it’s your home, workplace, or even another region or anywhere you have Internet access.
This allows you to access your devices and services, such as setting up a server type, installing video surveillance, or enabling Internet telephony.
To summarize, such a service will allow you to connect from the global network to the local one. How the connection will be used is up to the owner. If he wants, he will make a game server, connect a smart home, set up video surveillance, or do something else.
The main thing is not to forget about such openness risks.
Cons of a permanent IP (Static)
See the advantages in the scope because a permanent address will allow you to connect additional unavailable functions with a dynamic one. Each client’s advantages differ because many services rely on a reliable global address. Let’s talk about the cons now.
Once you’ve connected a static IP, setting up security is crucial because the network will become vulnerable to external attacks. With a static IP, you are open to connections from the wide area network (WAN). While this can be advantageous for various services, it also allows attackers to gain access.
In the case of dynamic, after each router reboot, you would receive a new identifier on the network. However, with a static IP, the old identifier remains constant. This means that passwords must constantly be reviewed, vulnerabilities discovered, and protection against DDoS attacks put in place to safeguard your equipment.
After configuring the static IP address, setting up a robust security system on your router is important. Consider separating your internal network from external connections, granting open access only to necessary folders and services while blocking the rest. We will not dwell on this in detail, but security must be taken seriously.
Private and Public IP
Now let’s talk about the “color” of IP because they are often mentioned on the network in this context. IPs can be categorized as white or gray or public and private IPs.
A public IP is displayed on the Internet, visible in the global network, and a whole subnet can sit through one address. On the other hand, private addresses are used within local networks of providers, companies, or individual users.
Did you know that private IPs are not routable on the Internet? Your provider assigns them, which can be found in your router or computer settings. These gray addresses are not directly visible on the Internet and are converted into public IPs through NAT, enabling information exchange.
By default, most of us have a gray address, which is safer because it allows multiple computers and routers to share a single public IP. On the other hand, white addresses are directly visible on the Internet. They are assigned immediately and bypass many intermediaries. This includes websites, public servers, and various online services.
Obtaining a white IP is a paid service for individuals due to limited availability and controlled issuance. So you have to purchase the right to use it from your provider, who acquires it from a regional registrar, and so on.
It’s fascinating how the Internet infrastructure works, isn’t it?
How to find out your IP and what it is?
If you do not know your static IP or dynamic, you have it dynamic. Go to the site whatismyipaddress.com, there on the main page, on the left side, you will see your address.
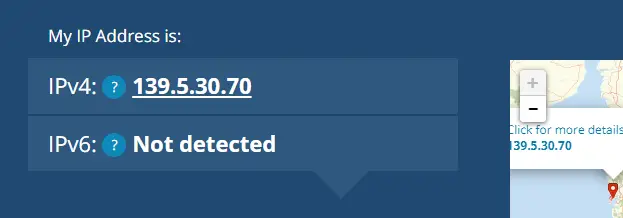
To accurately check if your IP is dynamic, follow these steps:
- Turn off your computer and router for 15 minutes, completely disconnecting them from the network.
- Turn them back on, and revisit the site.
- If the IP address has changed, it means you have a dynamic IP.
Please note that this method is simple and may not be completely accurate. For specific information, specific information will be given to you by your provider’s technical support.
- Read Also: Wifi Vs Internet, Difference Between Explained.
- Related: LAN vs WAN, vs MAN
Where and how to get a static IP?
You’ll need to contact your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to get a static IP. They’ll be able to tell you if it’s possible to get a static IP with your current plan or if you’ll need to upgrade.
Remember that there might be an extra cost associated with this. Once you’ve made the request, the ISP will assign you a unique, unchanging IP address, yours for as long as you keep that service.




There is definitely a lot to find out about this subject. I like all the points you made