Finding the right and compatible RAM for your PC can be a daunting task, especially if you are not familiar with the technicalities. Fortunately, there are a few things you can follow to pick the most compatible RAM for your PC.
But before that, let’s clear the basic specs of RAM.
Basic Specs of RAM
1. Type of RAM / DDR Generations
There are five types of DDR RAM: DDR, DDR2, DDR3, DDR4 and DDR5.
- DDR: This is the oldest and slowest type of RAM, also obsoleted.
- DDR2 & DDR3: These are faster than DDR but still older ones.
- DDR4: This is the most common type of RAM today since it was released in 2014. It offers higher speeds and better performance compared to its predecessors.
- DDR5: The newest addition to the list, DDR5 provides even higher speeds and better performance than DDR4. However, currently, it is only available in expensive motherboards.
Above mentioned standard types, in any case, are not compatible with each other since they have a different number of pins, voltage, and supported frequencies.
For example, DDR5 RAM type will not work on a motherboard that only supports DDR4. So, it’s essential to select the supported RAM generation for your motherboard before purchasing RAM.
2. Capacity
The capacity of RAM refers to how much memory it can hold. This is measured in gigabytes (GB), and the more GB your RAM has, the smoother your system will run with less clutter.
The minimum recommended RAM capacity for modern PCs is 8GB, but for better performance and multitasking, you may want to consider 16GB or even more if your budget allows.
Most budget motherboards today can accommodate up to 32GB of RAM, while high-end boards can support 64GB or 128 GB.
Regardless, 8GB of RAM may be enough for basic tasks like web browsing and document editing. Still, as soon as you start running more intensive programs like video editing or gaming, 8GB may not be sufficient.
16GB of RAM is commonly agreed upon as the sweet spot for most games, providing enough capacity for triple-A titles, multitasking, and running more demanding programs without breaking the bank.
On the other hand, having 32GB, 64GB, or more RAM is generally considered overkill and only necessary for specialized tasks like 3D rendering, professional video editing, or heavy multitasking.
4. Speed
RAM speed refers to how quickly it can transfer data during tasks also known as RAM frequency. This is measured in megahertz (MHz), and as a rule of thumb, the higher the MHz, the faster your system will process.
DDR4 RAM typically runs at speeds up to 4800MHz, while DDR5 RAM can reach up to 8200MHz. Higher speed means better performance and multitasking capabilities, but it also comes with a higher price tag.
It’s important to note that the high speed of your RAM can be limit by your motherboard which only supports lower speeds, then it will automatically underclock your RAM speed to match its maximum supported speed.
For example, if your motherboard only supports up to 3200MHz, getting a RAM with a speed of 4800MHz will still only run at 3200MHz.
5. Latency
RAM Latency refers to a set of four numbers, such as 16-18-18-36 – it is actually the time it takes for RAM to respond to the processor’s request, measured in nanoseconds.
The first number, known as CAS-latency or CL, is the most important and represents how many clock cycles it takes for RAM to respond to a request. The lower the number, the faster your system will perform.
Higher latency doesn’t necessarily mean poor performance, but it can impact certain tasks that require fast data transfer, like gaming or video editing.
What RAM is Compatible with my PC (2 Ways)
1. Through Motherboard Specs
Check your motherboard
Before you start looking for compatible RAM, one of the first things should you aware is the type of motherboard you have. Different motherboards have different requirements for RAM.
To find out, check the model number which is usually printed on the motherboard itself.
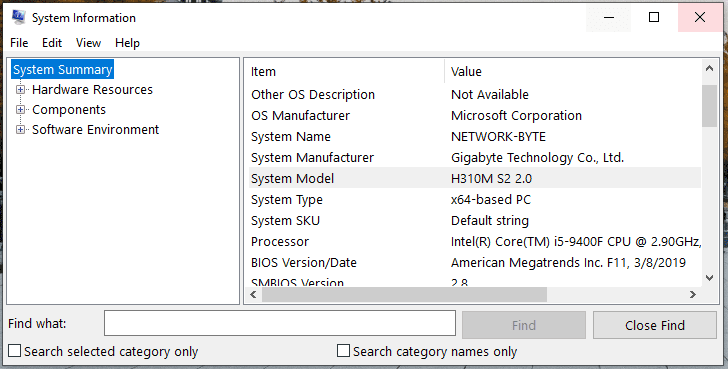
If a motherboard is already installed inside your PC, here’s how to find its product name in Windows:
- In Windows, click on the ‘Start’ button and type “system information” in the search box.
- Click on ‘System Information’ to open the application.
- Look for ‘BaseBoard Manufacturer’ and ‘BaseBoard Product’ under the System Summary tab. This will tell you the brand and model of your board.
You can also use a system information tool like CPU-Z to get detailed specifications of your PC.
Get Information on supported RAM types.
Once you identified model name or number, you can then look for its exact supported RAM modules through motherboard manufacturer website.
For instance, my motherboard model is ‘H310M S2 2.0’ from Gigabyte Technology, and I’d go to “Gigabyte.com” to look for this model and then the specs section. Or you can just do a quick Google search the motherboard’s model to find it.
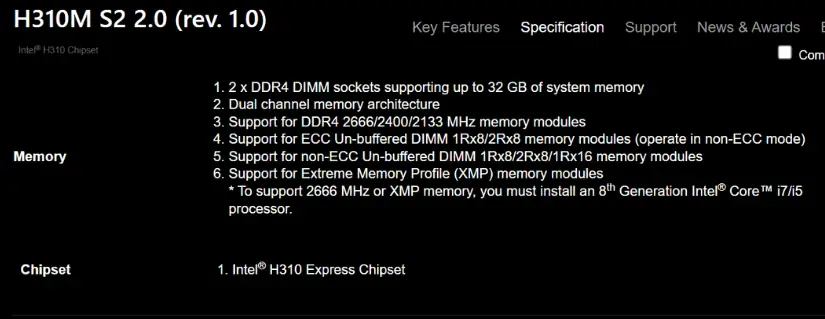
Here, the ‘GIGABYTE H310M S2 2.0’ motherboard supports DDR4 memory with speeds up to 3200MHz and 4733 MHz (O.C), holding up to 128 GB since it comes with four slots for RAM sticks (like 4×32 GB per stick), although I have no plans to use that much memory.
You will also find such information in the motherboard’s manual.
2. Check your Current RAM:
If you already have RAM installed on your PC, one thing you can do is find out what kind of RAM you have already so you can purchase the same type
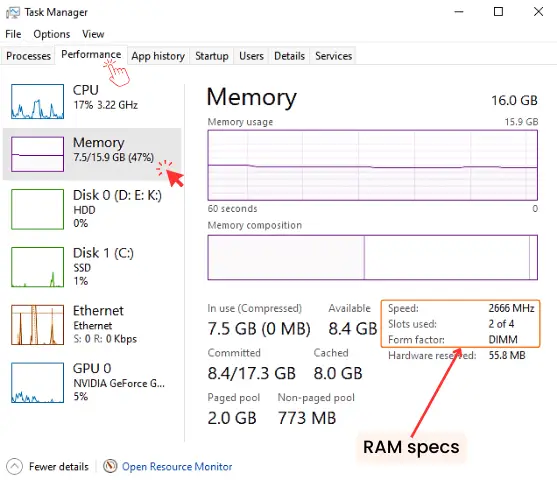
In Task Manager (for Windows users), you can find such information about your current RAM under the Performance tab and then the ‘Memory’ section on the left side.
You can also either use a system information tool like CPU-Z or look at the physical RAM sticks.
Here, knowing your current RAM’s speed, type, capacity, and the number of available slots will assists you in deciding new RAM needs and its type you can add to your system.
Remember Dual-Channel and Quad-Channel Configuration
When adding RAM to your system, it is essential to remember about the dual-channel and quad-channel configurations. This refers to how the RAM sticks are placed on the RAM slots.
For dual-channel configuration, two sticks of RAM with similar specifications should be installed in two slots for optimal performance. That means having two smaller capacity sticks (like 2×8 GB) will enhanced performance rather than one larger capacity stick (like 1×16 GB).
Similarly, in quad-channel configuration, four sticks of RAM with similar specifications should be installed in specific slots. That means having four smaller capacity sticks (like 4×8 GB) will provide better performance rather than two larger capacity sticks (like 2×16 GB) or one larger 32GB RAM bar.
Laptop (SODIMM) and Desktop (DIMM) RAM
When finding compatible RAM for your system, it is also important to mention the difference between laptop and desktop RAM.
Laptop RAM, also known as SODIMM (Small Outline Dual In-Line Memory Module), has a smaller form factor compared to desktop RAM, also known as DIMM (Dual In-Line Memory Module). This means that they are not interchangeable; just by looking at them, you can tell the size difference.

So, if you are planning for RAM upgrade on your laptop, make sure to purchase SODIMM sticks ‘Laptop RAM.’ In the case of the desktop’s RAM, make sure to get DIMM sticks.
Final Thoughts
When you find out what RAM is right, it should be a cost-effective, easy, and hassle-free upgrade. RAM is relatively cheap compared to other hardware upgrades and can significantly improve your system’s performance. Again, always make sure to buy RAM that is compatible with your motherboard.
Related




