I have already an article on ATX 3.0 PSU where I talk about the 12VHPWR connector and its features. However, in this article, we will be taking details of this specific connector and the technology that powers it.
Introduction to 12VHPWR
If you follow news about graphic cards, you might have heard about the recently introduced connector standard for them – 12VHPWR. To understand how it works and how it can be useful, let’s first find out where it came from and why now.
New connectors do not appear just like that; they solve the problems of existing ones and become new steps in their development. This means they also affect the operation of the devices they are connected to.
Definition of 12VHPWR
The 12VHPWR, or 12-Volt High Power Connector in power supply made for for high-demand components such as graphics cards. Unlike its predecessors, which primarily utilized 6-pin or 8-pin connectors, the 12VHPWR connector comes with a 16-pin configuration.
So, 12VHPWR is simply a connector with which the graphics card can be connected to the computer’s power supply.
Development and emergence of 12VHPWR
The need for a new connector arose from the development of graphics cards. If you have been at least a little interested in this market, you know that cards are becoming more powerful and demanding—requiring more space, energy, and better cooling. There are even jokes about video cards needing their own refrigerators soon.
This trend is understandable; video cards must deliver high-quality graphics and handle the load of modern games and graphics software. This load is shared by the motherboard, processor, and power supply. For instance, the RTX 3080Ti can consume up to 400W at peak, and the RTX 3090Ti up to 500W.
Previously, power connectors were limited, leading manufacturers to add multiple connectors to meet growing demands. However, this approach took up space, and graphics cards already require significant room inside systems.
Thus, a new 12VHPWR connector was created, first 12-pin and then 16-pin, which immediately made it possible to reduce the number of connectors on graphics cards. Users first saw it in 2022 with the Nvidia RTX 30 series, though designed with RTX4000 in mind. Initially, a 12-pin version without sense contacts was used, but the 16-pin version with these contacts soon became standard. We’ll talk about this in a little more detail later.
Appearance of the 12VHPWR connector and connector
We’ve sorted out the basics, and now let’s add some characteristics to the picture to better understand why the 12VHPWR connector is made the way it is now.
It is easy to distinguish it from others visually; it has one large 12-pin connector and several wires, usually 8-pin, extend from it. These are connectors for the power supply.

Physical characteristics
The 12VHPWR connector, with its 16-pin design, can deliver up to 600W of power to a graphics card. The “HPWR” in its name stands for “high power.” In contrast, an 8-pin connector provides only 150W, and a 6-pin connector delivers 75W.
On high-end GPUs, it was common to see space allocated for up to three 8-pin connectors, but adding more was often impractical. The 12VHPWR connector is a single rectangular block that houses six pairs of power connectors along with four additional sense connectors, optimizing power delivery and efficiency.
The connector here is 16-pin, but primary pins arranged in two rows of six. The upper connectors are designated for grounding, while the lower row contains the contact pins. The rated power is 684 W, although manufacturers specify a maximum of 600 W.
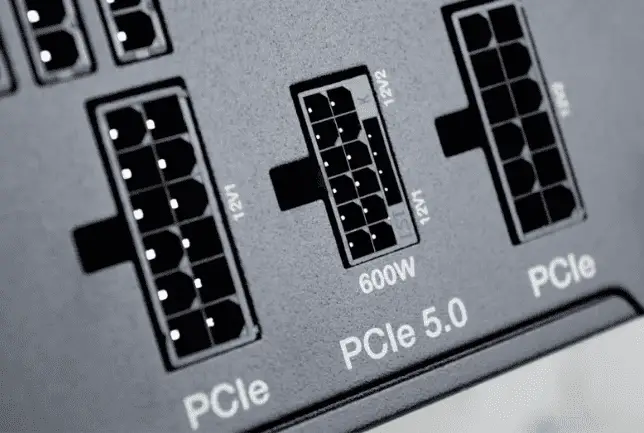

The rated output current is 9.5 A, compared to 7-8 A for an 8-pin connector. Additionally, there are 4 smaller pins, separate from the main ones, known as “sense” contacts. These enhance the safety of the connection between the power supply and the video card, ensuring the connector is securely attached before installation. This connector adheres to PCIe 5.0 and ATX 3.0 standards.
High power support
Of course, the main advantage of the new connector is the ability to cope with heavy loads and power consumption of up to 600 W. This is an excellent opportunity for top-end video cards, since a pair of connectors could replace 3 or even more at once.
And everything would be fine if it weren’t for the fact that the connector itself can melt if the load, and therefore the temperature of the video card, is too high. This caused quite a big controversy, because damage to the connector during operation of the video card can, at a minimum, damage the card itself, and at maximum, cause damage to the entire computer.
They even attempted to shift the blame onto the users, claiming that improper handling—such as excessively bending the cables or not fully inserting the connector—led to poor connections. While this might be an issue for some users, it is unlikely to be a widespread problem.
A study of the 12VHPWR design showed that its developers were not entirely right. In their effort to make the connector as compact as possible, they compromised on the reliability and safety of the contacts.
Compatible with other devices
Today, adapters or extension cables are available that enable the use of 8-pin connectors as 16-pin ones, allowing more devices to accommodate the new standard. However, the appearance of these connectors can vary depending on the manufacturer. Many today, for example, care not so much about design as about the correct bending of cables.
Conclusion
The developers had a clear goal: to simplify life for users and optimize product design. And the idea was good, the implementation just let us down. Although some users believe that it was not worth developing 8-pin connectors at all and replacing them with others of a new type. I will also talk about 12VHPWR and how you can ensure the safety of their use if you become the owner of such a connector.
- Related: How long do Power Supplies Last? Average Lifespan of PSUs?
- Also Read: Comparison of RTX 30 series and 40 series GPUs