Modern computers are super high-performance and designed to keep your data safe. But, they’re still machines, right?
There is a possibility that data may be lost due to a problem. Like, a power outage are one of the problems that affect computers, and data on your computer may be lost due to a power outage.
Therefore, this time we will introduce UPS as a measure to prevent data loss due to power outages.
Data lost on a Computer due to a Power Outage?
In the case of a desktop computer, if the power supply gets cut off due to a power outage, everything you were working on might suddenly disappear without saved. But don’t worry, the data that you’ve already saved is usually safe.
However, if the power goes out while your computer is reading or writing to the hard disk, things can get messy. Like, physically damaged hard disk kind of messy. And that means losing all the precious data stored on it.
In the worst-case scenario, you might even have to replace the whole hard disk and start from scratch, reinstalling the operating system and all the applications.
Previously saved data cannot be retrieved unless you back it up. There are also cases where components besides the hard disk might get damaged too. In that case, you’ll probably have to buy a new computer.
A UPS to protect your computer from Power Outages!
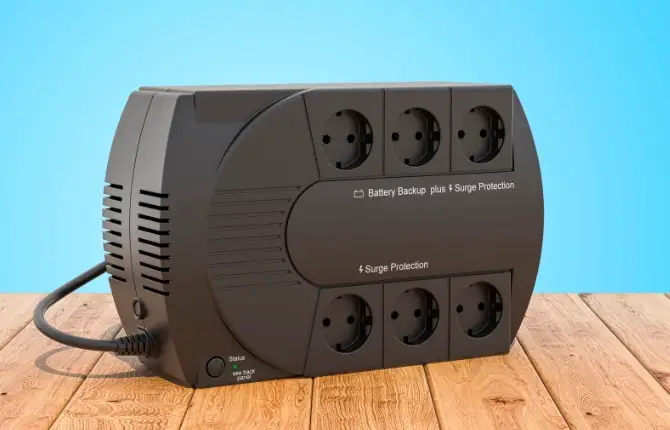
Wondering how to prevent data loss or computer failure due to power outages? Here’s a tip: consider using a UPS (uninterruptible power supply). It’s a device with a built-in battery that supplies power to your computer when it detects a power problem, like an outage.

So, even if the lights go out, your computer stays powered on and you can keep working for a while. During this time, you can protect your computer by saving any necessary data and shutting it down properly.
A regular UPS can power multiple devices, making it a handy backup solution not just for your computer, but also for routers, external hard drives for backups, and more.
Many companies install UPS to prevent data loss. Although it may seem like a high hurdle to introduce into a general household, in recent years UPSs have appeared that can be easily used just like regular power strips.
Also, since it is affordable and can be easily installed in any home. It’s a good idea to have one in case of a outage or even surge as it can power other devices too. Just remember to check if there are some devices that are not recommended to be connected to a UPS, so be sure to check before installing them.
Type of UPS
There are several types of UPS that protect your computer during a power outage. So, let’s introduce the differences between them.
1. Constant commercial power supply method
The continuous commercial power supply method is the most common type of UPS. Under normal conditions, power is sent directly from the commercial power source to the computer without going through the battery, and in the event of a power outage, power is supplied from the battery.
When an abnormality occurs in the commercial power supply due to a power outage, the system switches to battery power, resulting in a momentary power outage (momentary power outage), but computers are not affected by the power outage. This constant commercial power supply method is the cheapest method in terms of price.
2. Constant inverter power supply system
The continuous inverter power supply method is a method that constantly providing power via an inverter (device that converts direct current to alternating current). Unlike regular power supply systems, there won’t be any momentary power outage when switching to battery power.
Normally, power from the commercial power supply is sent to both the inverter and the battery power supply. And if there’s a failure in the commercial power supply, the stored power in the battery is supplied through the inverter.
As mentioned above, for computers, there is basically no problem even if a momentary power outage occurs.
However, a constant inverter power supply system is used for precision equipment that is likely to be affected by momentary power outages. Just keep in mind that this method offers higher performance but also comes with a higher price tag.
3. Line interactive method
The line interactive method works just like the continuous commercial power supply method. Basically, it means that the computer gets power directly from the commercial power supply most of the time, but when there’s a power outage, it switches to the battery power supply.
However, the line interactive method is equipped with a transformer that adjusts the voltage, so it can keep the output voltage steady even if there are voltage fluctuations during a power outage.
Although momentary power outages do occur, their duration is short and a more stable power supply is possible. Although the line interactive method is not as powerful as the constant inverter power supply method, but it’s a bit pricier.
How to choose a UPS is for home computers?

So, what kind of UPS is suitable for home computers?
The most stable power supply option is the constant inverter powered UPS. However, they can be quite expensive and have over-specs for most home computers.
Therefore, I suggest considering a constant commercial power supply system or a line interactive system UPS instead.
Actually, many UPS devices designed for home use either a constant commercial power supply method or a line interactive method. Not only is it cheap, but also compact in size, just like a regular power strip.
Speaking of which, battery capacity is a crucial factor to consider when selecting a UPS. For power outage protection for your home desktop computer, a capacity of around 1,000VA should suffice. With this capacity, a typical home computer can run for approximately 10 to 20 minutes. So, it’s a good idea to save any work you’re doing and shut down during this time.
- Read Also: How long do Power Supplies Last? Average Lifespan of PSUs?
- Related: Guide to Cheap Computer Upgrades from 0, 20$ to 50$
If you’re looking to connect multiple computers or other devices, opt for a UPS with a larger capacity. However, do keep in mind that higher capacity means a higher price tag and a larger physical size. So, choose wisely according to the purpose.